Cerenia hund

THANKS FOR YOUR ANSWER!

Read on to learn more about how CERENIA ® (maropitant citrate) can help.
TAKE CARE OF YOUR PET'S VOMITING


Th e Misadven tures
For any dog or cat, vomiting can be a painful, exhausting, anxiety-inducing experience. 1 Though there may be many causes, there is only one FDA-approved treatment.
CERENIA ® (maropitant citrate) is the first and only FDA-approved veterinary medication to safely and effectively treat vomiting in dogs and cats and prevent vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs.*
CERENIA Users 2
Th e Misadven tures o f Ralph
Car sickness affects as many as 20% of dogs. 3

Important Safety Information:
Use CERENIA Injectable for vomiting in cats 4 months and older; use subcutaneously for acute vomiting in dogs 2 to 4 months of age or either subcutaneously or intravenously in dogs 4 months of age and older. Use CERENIA Tablets for acute vomiting in dogs 2 months and older, and for prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs 4 months and older. Safe use has not been evaluated in cats and dogs with gastrointestinal obstruction, or those that have ingested toxins. Use with caution in cats and dogs with hepatic dysfunction. Pain/vocalization upon injection is a common side effect. In people, topical exposure may elicit localized allergic skin reactions, and repeated or prolonged exposure may lead to skin sensitization. See full Prescribing Information.
- BarkBox is a registered trademark of BarkBox, Inc.
- Benadryl® is a registered trademark of Johnson & Johnson Consumer Inc. or one of its affiliated companies. Dramamine® is a registred trademark of Prestige Brands Holdings, Inc. or its licensors. Bonine® is a registered trademark of Insight Pharmaceuticals LLC.
- * Dramamine®, Bonine®, Benadryl® and herbal supplements have not been tested and approved by the FDA-CVM for use in dogs.
- 1 Conder GA, Sedlacek HS, Boucher JF, Clemence RG. Efficacy and safety of maropitant, a selective neurokinin 1 receptor antagonist, in two randomized clinical trials for prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2008;31(6):528-532.
- 2 Data on file, Cerenia A&U Report June 2016. Zoetis Inc.
- 3 Data on file, Harris Interactive Pet Owner Market Research CERMS2012, 2012 Zoetis Inc.
- 4 Yates BJ, Miller AD, Lucot JB. Physiological basis and pharmacology of motion sickness: an update. Brain Res Bull. 1998;47(5):395-406.
Online Product Information Statement:
The product information provided in this site is intended only for residents of the United States. The products discussed herein may not have marketing authorization or may have different product labeling in different countries. The animal health information contained herein is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace discussions with an animal healthcare professional. All decisions regarding the care of a veterinary patient must be made with an animal healthcare professional, considering the unique characteristics of the patient.
All trademarks are the property of Zoetis Services LLC or a related company or a licensor unless otherwise noted. ©2017 Zoetis Services LLC. All rights reserved. CER-00284R1
Treat or Prevent Vomiting
With Once-Daily CERENIA
CERENIA ® (maropitant citrate), the first and only FDA‑approved veterinary antiemetic, effectively treats or prevents canine and feline vomiting from multiple causes. 1,2
CERENIA Is the #1 Antiemetic Prescribed for Cats and Dogs
Rapid onset of action and 24-hour efficacy 3-6
Easy once-daily dosing
Unique mode of action
that treats or prevents vomiting from multiple causes 3, 7-9
Feline Vomiting
Vomiting can have various causes. Address your feline patients' immediate needs while diagnosing the underlying cause of the vomiting.
Perioperative Vomiting in Dogs
Prevent vomiting when using opioids in your canine preoperative protocol.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION: Use CERENIA Injectable for vomiting in cats 4 months and older; use subcutaneously for acute vomiting in dogs 2 to 4 months of age or either subcutaneously or intravenously in dogs 4 months of age and older. Use CERENIA Tablets for acute vomiting in dogs 2 months and older, and for prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs 4 months and older. Safe use has not been evaluated in cats and dogs with gastrointestinal obstruction, or those that have ingested toxins. Use with caution in cats and dogs with hepatic dysfunction. Pain/vocalization upon injection is a common side effect. In people, topical exposure may elicit localized allergic skin reactions, and repeated or prolonged exposure may lead to skin sensitization. Please see full Prescribing Information.
The product information provided in this site is intended only for residents of the United States. The products discussed herein may have different labeling in different countries. The animal health information contained herein is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace discussions with an animal healthcare professional. All decisions regarding the care of a veterinary patient must be made with an animal healthcare professional, considering the unique characteristics of the patient.
All trademarks are the property of Zoetis Services LLC or a related company or a licensor unless otherwise noted.
Zoetis Services LLC. All rights reserved. CER-00225RI
- Create Account
- News & Media
- Contact Us
- ABOUT US
- RESPONSIBILITY
- Commitment To Veterinarians
- Responsible Use Of Antibiotics
- Diversion Policy
- PRODUCTS & SERVICES
- Animal Genetics
- CLARIFIDE
- Enlight
- GeneMax Advantage
- GeneMax Focus
- HD 50K
- i50K
- PredicGen
- View All Products
- Beef
- BOVI-SHIELD®
- CATTLEMASTER GOLD FP® 5
- CATTLEMASTER GOLD FP® 5 L5
- DECTOMAX® INJECTABLE
- DECTOMAX® POUR-ON-SOLUTION
- EXCEDE®
- INFORCE™ 3
- VIEW ALL PRODUCTS
- Cats & Dogs
- APOQUEL
- CYTOPOINT
- CERENIA®
- CLAVAMOX®
- CONVENIA®
- FELOCELL® 3
- FLUID THERAPY
- PROHEART®6
- REVOLUTION®
- RIMADYL®
- SIMBADOL
- VANGUARD®CRLYME
- VANGUARD® PLUS 5 L4
- ZENIQUIN®
- View All Products
- Dairy
- BOVI-SHIELD®
- EXCEDE®
- EXCENEL® RTU EZ
- FACTREL Injection
- INFORCE™ 3
- LUTALYSE®
- LUTALYSE® HighCon
- SPECTRAMAST® LC
- SPECTRAMAST® DC
- View All Products
- Diagnostics
- Food Safety
- Horses
- DORMOSEDAN®
- EXCEDE®
- FLUVAC INNOVATOR®
- QUEST®/QUEST® Plus Gel
- SOLITUDE® IGR
- STRONGID® C/C 2X
- STRONGID® Paste
- WEST NILE-INNOVATOR®
- View All Products
- Pork
- DRAXXIN®
- EXCEDE® FOR SWINE
- Flusure XP
- Fostera® PCV MH
- Fostera® PRRS
- Improvest ®
- LINCOMIX® Feed Medication
- RESPISURE-ONE®
- View All Products
- Poultry
- Bursine®-2
- Poulvac Maternavac® IBD-Reo
- Poulvac® E coli
- Poulvac® Myco F
- Poulvac® SE-ND-IB
- Poulvac® SE-ND-IB
- View All Products
- Reproduction Services
- Services
- PeopleFirst
- Pet Wellness Report
- Profit Solver
- View All Products
- Sheep
- EAZI-BREED ™ CIDR ® Sheep Insert
- View All Products
- Animal Genetics
- PROGRAMS
- Salmonella Prevention
- ID MYHORSE
- Individual Pig Care
- LifeLong Care
- Veterinary Medical Information & Product Support
- Zoetis For Shelters
- SOCIAL & APPS
- ELEARNING
- VETVANCE
- Zoetis eLearning
- BILL PAY
- SHOP NOW
- CONNECT WITH US
- Contact Us
- YouTube
All trademarks are the property of Zoetis Services LLC or a related company or a licensor unless otherwise noted.
Cerenia hund
Already have a VetUK Account?
Don't have an account?
Cerenia Tablets for dogs contain 16 mg, 24 mg, 60 mg or 160 mg maropitant as maropitant citrate monohydrate. The tablets also contain Sunset Yellow (E110) as a colourant. The tablets are pale orange and have a score line on both sides allowing the tablet to be halved. Each tablet is marked with the Pfizer logo on the reverse side. On the obverse side, each half is marked with the letters "MPT" and figures denoting the quantity of maropitant.
Cerenia 160mg Tablet
Cerenia tablets contain boxmaropitant citrate monohydrate. Indicated for the prevention of vomiting including that induced by chemotherapy, in conjunction with cerenia solution for. [More info]

Cerenia 16mg Tablet
Cerenia tablets contain boxmaropitant citrate monohydrate. Indicated for the prevention of vomiting including that induced by chemotherapy, in conjunction with cerenia solution for. [More info]

Cerenia 24mg Tablet
Cerenia tablets contain boxmaropitant citrate monohydrate. Indicated for the prevention of vomiting including that induced by chemotherapy, in conjunction with cerenia solution for. [More info]

Cerenia 60mg Tablet
Cerenia tablets contain boxmaropitant citrate monohydrate. Indicated for the prevention of vomiting including that induced by chemotherapy, in conjunction with cerenia solution for. [More info]
Cerenia tablets are indicated for the prevention of nausea induced by chemotherapy. For the treatment of vomiting, in conjunction with Cerenia Solution for Injection and in combination with other supportive measures. For the prevention of vomiting including that induced by motion sickness.Also the prevention of nausea induced by chemotherapy and treatment and prevention of vomiting (except motion sickness)
Cerenia tablets should be administered once daily, at a dose of 2 mg maropitant per kg bodyweight, using the number of tablets given in the table below. Tablets are breakable along the score line on the tablet.
To prevent vomiting, tablets should be given more than 1 hour in advance. The duration of the effect is approximately 24 hours and, therefore, tablets can be given the night before administration of an agent that may cause emesis (e.g. chemotherapy).
Cerenia can be used as either tablets or Solution for Injection once daily for up to five consecutive days to treat vomiting.
Cerenia tablets are effective in the treatment of vomiting, however in cases of frequent vomiting it is recommended to initiate treatment with Cerenia Solution for Injection.
Treatment and prevention of vomiting (except motion sickness)
Cerenia tablets should be administered once daily, at a dose of 8 mg maropitant per kg bodyweight, using the numbers of tablets given in the table below. Tablets are breakable along the score line on the tablet.
Tablets should be administered at least one hour before starting the journey. The anti-emetic effect persists for at least 12 hours, which for convenience may allow administration the night before early morning travel. Treatment may be repeated for a maximum of two consecutive days.
In some individual dogs and when repeating the treatment, lower doses than recommended might be sufficient.
Prevention of motion sickness only
Firstly, fold or cut along the perforation between each tablet as shown by the scissor symbol. Find the pull-back notch (or cut) as shown by the arrow symbol. Holding one side of the cut firmly, pull the other side towards the centre of the blister until the tablet is visible. Remove table from blister and administer as instructed.
Note: No attempt should be made to remove the tablet by pushing it through the blister backing as this will damage both the tablet and blister.
A light meal or snack before dosing is recommended; prolonged fasting before administration should be avoided. Cerenia tablets should not be administered wrapped or encapsulated in food as this may delay dissolution of the tablet and consequently the onset of the effect.
Dogs should be carefully observed following administration to ensure that each tablet is swallowed.
Vomiting can be associated with serious, severely debilitating conditions including gastrointestinal obstructions; therefore, appropriate diagnostic evaluations should be employed.
Administering Cerenia on a completely empty stomach may cause the dog to vomit. A light snack before dosing could help prevent this effect.
The safety of Cerenia has not been established in dogs less than 16 weeks of age and in pregnant or lactating bitches. Use only according to a risk benefit assessment by the responsible veterinary surgeon.
Cerenia should be used in conjunction with other supportive measures if appropriate.
Clinical signs including vomiting on first administration, excess salivation and watery faeces have been observed when the product has been overdosed in excess of 20 mg/kg.
Maropitant is metabolised in the liver and therefore should be used with caution in dogs with liver disease.
Cerenia should be used with caution in animals suffering from or with a predisposition for heart diseases. Cerenia should not be used concomitantly with Ca-channel antagonists as maropitant has affinity to Ca-channels.
Maropitant is highly bound to plasma proteins and may compete with other highly bound drugs.
Cerenia is not a sedative and some motion sick dogs may show nausea-like signs during travel such as salivation and lethargy. These signs are temporary and should resolve when the journey ends.
Incidents of pre-travel vomiting, usually within two hours post-dosing, were commonly reported after administration of the 8 mg/kg dose.
Wash hands after use. In case of accidental ingestion seek medical advice immediately and show the package leaflet or the label to the physician.
This veterinary medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions.
Half tablets should be stored for a maximum of two days after removal from the blister. Half-tablets should be returned to the opened blister and kept within the cardboard outer.
Any unused veterinary medicinal product or waste materials derived from such veterinary medicinal products should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children. For animal treatment only.
Cerenia tablets are supplied in blister packs with four tablets per pack.
Cerenia ®
For subcutaneous injection in dogs and cats
Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
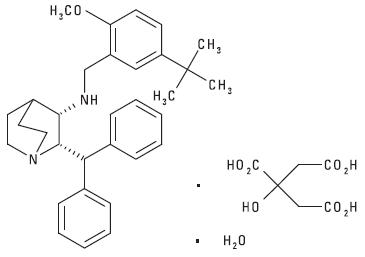
Maropitant is a neurokinin (NK1) receptor antagonist that blocks the pharmacological action of substance P in the central nervous system (CNS). Maropitant is the non-proprietary designation for a substituted quinuclidine. The empirical formula is C32H40N2O C6H8O7 H2O and the molecular weight 678.81. The chemical name is (2 S ,3 S) -2-benzhydryl- N -(5- tert -butyl-2- methoxybenzyl) quinuclidin-3-amine citrate monohydrate. Each mL of CERENIA Injectable Solution contains 10 mg maropitant, 63 mg sulphobutylether-beta-cyclodextrin, 3.3 mg meta-cresol and water for injection.
The chemical structure of maropitant citrate is:

INDICATIONS
Dogs: CERENIA (maropitant citrate) Injectable Solution is indicated for the prevention and treatment of acute vomiting in dogs.
Cats : CERENIA (maropitant citrate) Injectable Solution is indicated for the treatment of vomiting in cats.
Dosage and Administration
Use of refrigerated product may reduce the pain response associated with subcutaneous injection.
Dogs 4 months of Age and Older : Administer CERENIA Injectable Solution intravenously over 1-2 minutes or subcutaneously at 1 mg/kg (0.45 mg/lb) equal to 0.1 mL/1 kg (1 mL/22 lb) of body weight once daily for up to 5 consecutive days.
In dogs that are actively vomiting, it is recommended to initiate treatment with CERENIA Injectable Solution. Thereafter, CERENIA Tablets may be used for the prevention of acute vomiting at 2 mg/kg once daily. (See CERENIA Tablets package insert for complete prescribing information).
For Prevention of Vomiting in Dogs 4 months of Age and Older Caused by Emetogenic Medications or Chemotherapeutic Agents: Administer CERENIA Injectable Solution intravenously over 1-2 minutes or subcutaneously at 1 mg/kg (0.45 mg/lb) of body weight one time, 45-60 minutes prior to use of emetogenic medications or chemotherapeutic agents.
For Treatment of Vomiting in Cats 4 Months of Age and Older: Administer CERENIA Injectable Solution intravenously over 1-2 minutes or subcutaneously at 1 mg/kg (0.45 mg/lb) equal to 0.1 mL/kg (0.1 mL/2.2 lb) of body weight once daily for up to 5 consecutive days.
The underlying cause of acute vomiting should be identified and addressed in dogs and cats that receive CERENIA Injectable Solution. If vomiting persists despite treatment, the case should be re-evaluated.
Not for use in humans. Keep out of reach of children. In case of accidental injection or exposure, seek medical advice. Topical exposure may elicit localized allergic skin reactions in some individuals. Repeated or prolonged exposure may lead to skin sensitization. In case of accidental skin exposure, wash with soap and water. CERENIA is also an ocular irritant. In case of accidental eye exposure, flush with water for 15 minutes and seek medical attention.
In puppies younger than 11 weeks of age, histological evidence of bone marrow hypocellularity was observed at higher frequency and greater severity in puppies treated with CERENIA compared to control puppies. In puppies 16 weeks and older, bone marrow hypocellularity was not observed ( see ANIMAL SAFETY ).
PRECAUTIONS
The safe use of CERENIA Injectable Solution has not been evaluated in dogs or cats with gastrointestinal obstruction or that have ingested toxins.
Use with caution in patients with hepatic dysfunction because CERENIA Injectable Solution is metabolized by CYP3A, CYP2D15(dogs) and CYP1A (cats) enzymes (see Pharmacokinetics ). The influence of concomitant drugs that may inhibit the metabolism of CERENIA Injectable Solution has not been evaluated. CERENIA Injectable Solution is highly protein bound. Use with caution with other medications that are highly protein bound. The concomitant use of CERENIA Injectable Solution with other protein bound drugs has not been studied in dogs or cats. Commonly used protein bound drugs include NSAIDs, cardiac, anticonvulsant, and behavioral medications. Drug compatibility should be monitored in patients requiring adjunctive therapy.
The safe use of CERENIA Injectable Solution has not been evaluated in dogs or cats used for breeding, or in pregnant or lactating bitches or queens.
Adverse Reactions
In a US field study for the prevention and treatment of vomiting associated with administration of cisplatin for cancer chemotherapy, the following adverse reactions were reported in 77 dogs treated with CERENIA Injectable Solution at 1 mg/kg subcutaneously or 41 dogs treated with placebo:
The following adverse reactions were reported during the course of a US field study for the prevention and treatment of acute vomiting in dogs treated with 1 mg/kg CERENIA Injectable Solution subcutaneously and/or CERENIA Tablets at a minimum of 2 mg/kg orally once daily for up to 5 consecutive days:
Other clinical signs were reported but were <0.5% of dogs.
Adverse reactions seen in a European field study included ataxia, lethargy and injection site soreness in one dog treated with CERENIA Injectable Solution.
Post-Approval Experience (Rev. 2015)
The following adverse events are based on post-approval adverse drug experience reporting. Not all adverse events are reported to FDA CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using these data.
The following adverse events reported for dogs are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency for CERENIA Injectable Solution: Pain/vocalization upon injection, depression/lethargy, anorexia, anaphylaxis/anaphylactoid reactions (including swelling ofthe head/face), ataxia, convulsions, hypersalivation, tremors, fever, dyspnea, collapse/loss of consciousness, recumbency, injection site reactions (swelling, inflammation) and sedation.
Cases of death (including euthanasia) have been reported.
The following adverse reactions were reported during the course of a US field study for the treatment of vomiting in cats treated with 1 mg/kg CERENIA Injectable Solution subcutaneously once daily for up to five consecutive days:
The clinician observed and graded each cat’s response to injection.
2 Cat objected to the injection by retreating and vocalizing
3 Cat objected to the injection by retreating, hissing, scratching,
Post-Approval Experience (Rev. 2015)
The following adverse events are based on post-approval adverse drug experience reporting. Not all adverse events are reported to FDA CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using these data.
The following adverse events reported for cats are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency for CERENIA Injectable Solution: Depression/lethargy, anorexia, hypersalivation, pain/vocalization upon injection, dyspnea, ataxia, fever, recumbency, vomiting, panting, convulsion, and muscle tremor.
Cases of death (including euthanasia) have been reported.
To report suspected adverse events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the SDS, contact Zoetis Inc. at 1-888-963-8471 or www.zoetis.com.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or online at http://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/SafetyHealth.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Pharmacodynamics:
Vomiting is a complex process coordinated centrally by the emetic center which consists of several brainstem nuclei (area postrema, nucleus tractus solitarius, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus) that receive and integrate sensory stimuli from central and peripheral sources and chemical stimuli from the circulation and the cerebro-spinal fluid. Maropitant is a neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonist which acts by inhibiting the binding of substance P, a neuropeptide of the tachykinin family. Substance P is found in significant concentrations in the nuclei comprising the emetic center and is considered the key neurotransmitter involved in emesis.1 By inhibiting the binding of substance P within the emetic center, maropitant provides broad-spectrum effectiveness against neural (central) and humoral (peripheral) causes of vomiting. In vivo model studies in dogs have shown that maropitant has antiemetic effectiveness against both central and peripheral emetogens including apomorphine, cisplatin, and syrup of ipecac.
Pharmacokinetics
CERENIA Injectable Solution is formulated using sulphobutyletherß-cyclodextrin (SBECD), which exhibits enhanced binding to maropitant at refrigerated temperatures. The enhanced binding affinity reverses rapidly upon warming.
The pharmacokinetic (PK) characterization associated with maropitant after a single oral (PO), intravenous (IV), or subcutaneous (SC) dose administration in adult Beagle dogs is provided in the table below.
a Harmonic mean
The absolute bioavailability of maropitant was much higher following SC injection (91% at 1 mg/kg) than after PO administration (24% at 2 mg/kg). Oral bioavailability may be underestimated due to the presence of nonlinear kinetics and the resulting longer T1/2 seen after intravenous (IV) administration. Although hepatic firstpass metabolism contributed to the relatively low bioavailability after an oral dose, prandial status does not significantly affect the extent of oral bioavailability. Greater than dose-proportional drug exposure can be expected with an increase in dose (1–16 mg/kg PO). Systemic clearance of maropitant following IV administration was 1499.13 mL/hr/kg at a dose of 1 mg/kg. An accumulation ratio of 1.5 was observed following once-daily use of maropitant for five consecutive days at 1 (SC) or 2 mg/kg (PO). Urinary recovery of maropitant and its major metabolitewas minimal (<1% each). The hepatic metabolism of maropitant involves two cytochrome P-450 isoenzymes: CYP2D15 and CYP3A12. Based on in vitro enzyme kinetics data, it is believed that the non-linear kinetics may be partially associated with saturation of the low capacity enzyme (CYP2D15). However as doses increase (20–50 mg/kg PO), dose proportionality is re-established. Based upon in vitro enzyme kinetics, involvement of a high capacity enzyme (CYP3A12) may contribute to this return to dose linearity. Plasma protein binding of maropitant was high (99.5%).
Based on differences in plasma trough concentrations from a single study, the exposure of 10 week old puppies to maropitant may be lower than that observed in adult dogs, particularly after doses of 1 or 2 mg/kg.
The pharmacokinetic characterization associated with maropitant after a single subcutaneous (SC) or intravenous (IV) dose administration in cats is provided in the table below.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters for a Single Dose in 6-7 Month Old Cats (Mean±SD or Mean and Range)

There appears to be an age-related effect on the pharmacokinetics of maropitant in cats; kittens (4 months) have a higher clearance than adults. In multiple IV and SC studies, the mean maropitant half-life in kittens (4-7 months old) is 7.83 hours, compared to 17.2 hours in adults. The mean bioavailability of maropitant after subcutaneous administration in cats was 91.3%. The mean total body clearance (CL) and volume of distribution at steady-state (Vss) determined after IV administration of 1.0 mg/kg to 6 cats was 510 (388 to 603) mL/hr/kg and 2.3 (1.4 to 3.6) L/kg, respectively. Maropitant displays linear kinetics when administered SC within the 0.25–3 mg/kg dose range. Following SC administration of once daily doses of 1 mg/kg body weight for 5 consecutive days, accumulation was 250%. Maropitant undergoes cytochrome P450 (CYP) metabolism in the liver. CYP1A and CYP3A-related enzymes were identified as the feline isoforms involved in the hepatic biotransformation of maropitant. Renal and fecal clearances are minor routes of elimination for maropitant, with less than 1% of a 1 mg/kg SC dose appearing in the urine or feces as maropitant. For the major metabolite, 10.4% of the maropitant dose was recovered in urine and 9.3% in feces. Plasma protein binding of maropitant in cats was estimated to be 99.1%.
EFFECTIVENESS
In laboratory model studies, CERENIA Injectable Solution administered at 1 mg/kg in Beagle dogs reduced the number of emetic events associated with established neural (central) and humoral (peripheral) stimuli. Following administration of apomorphine (central emetic stimuli), vomiting was observed in 16.7% (2 of 12) of dogs treated with CERENIA Injectable Solution and 83.3% (10 of 12) of placebo-treated dogs. Following administration of syrup of ipecac (peripheral emetic stimuli) vomiting was observed in 25% (3 of 12) of dogs treated with CERENIA Injectable Solution and in 100% (12 of 12) of dogs treated with placebo.
In a study of veterinary cancer patients, dogs were treated with CERENIA Injectable Solution or placebo either 1 hour prior to cisplatin (prevention) or after the first vomiting episode following cisplatin (treatment) and monitored for 5 hours. In the groups evaluated for prevention of vomiting, 94.9% (37/39) of the dogs administered CERENIA Injectable Solution and 4.9% (2/41) of the dogs administered placebo did not vomit. In the groups evaluated for treatment, 21% (8/38) of the dogs administered CERENIA Injectable Solution and 5.1% (2/39) of the dogs administered placebo had no further episodes of vomiting following treatment.
In a study of 275 canine patients presented to veterinary hospitals with a history of acute vomiting, dogs were initially administered CERENIA Injectable Solution or placebo on Day 0. Following the initial dose, dogs allocated to the CERENIA group were treated with either CERENIA Tablets at a minimum of 2 mg/kg orally or Injectable Solution at 1 mg/kg subcutaneously once daily at the discretion of the clinician. Dogs allocated to the placebo group were treated using either an injectable placebo solution or placebo tablets once daily at the discretion of the clinician. Of the 199 dogs included in the analysis for effectiveness, 27 of 54 dogs (50%) in the placebo group displayed vomiting at some time during the study and 31 of 145 dogs (21.4%) in the CERENIA-treated group displayed vomiting during the study period.
In US field studies in veterinary patients, CERENIA Injectable Solution and Tablets were well tolerated in dogs presenting with various clinical conditions including parvovirus, gastroenteritis, and renal disease. There were no notable differences in mean laboratory values between CERENIA-treated and placebo-treated patients.
CERENIA Injectable Solution was used safely in dogs receiving other frequently used veterinary products such as fluid and electrolyte replacement solutions, antimicrobial agents, vaccines, antacids, and antiparasitic agents.
In a laboratory study, thirty-one dogs were subcutaneously administered CERENIA Injectable Solution or saline, at 1 mL/10 kg body weight, 45 minutes prior to administration of an opioid analgesic. Following administration of the opioid analgesic, none of the CERENIA Injectable Solution treated dogs vomited and 93.8% (15/16) of placebo-treated dogs vomited.
The effectiveness of CERENIA administered at 1 mg/kg IV was demonstrated by bridging the results of a PK study to clinical data supporting effectiveness of 1 mg/kg administered SC. The IV and SC administration of a single dose of 1 mg/kg maropitant are equivalent, based on the bioequivalence of the IV and SC AUClast and justification for the therapeutic equivalence of the IV and SC Cmax.
In a field study, 195 cats were presented to veterinary hospitals with a history of vomiting associated with various clinical conditions including gastroenteritis, gastritis, pancreatitis, inflammatory bowel disease, neoplasia, and hepatic lipidosis. Cats were treated with CERENIA Injectable Solution or placebo (in a ratio of 2:1) and observed in the veterinary hospital for 24 hours for the presence of an emetic event(s) defined as the observation of the act of vomiting or the presence of vomitus. Cats could continue antiemetic treatment every 24 hours for up to 5 consecutive days at the discretion of the clinician. Of 165 cats included in the analysis for effectiveness, 2 CERENIA-treated cats (1.8%) vomited 1 time each and 10 placebo-treated cats (18.5%) vomited a total of 15 times in the first 24 hours post treatment.
Percent of Cats Vomiting for Each Study Day by Treatment
The effectiveness of CERENIA administered at 1 mg/kg IV was demonstrated by bridging the results of a PK study to clinical data supporting effectiveness of 1 mg/kg administered SC. The IV and SC administration of a single dose of 1 mg/kg maropitant are equivalent, based on the bioequivalence of the IV and SC AUC last and justification for the therapeutic equivalence of the IV and SC Cmax
ANIMAL SAFETY
Laboratory and field studies have demonstrated that CERENIA Injectable Solution is well tolerated in dogs after subcutaneous administration.
Fifty six Beagle dogs (28 males and 28 females) approximately 16 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Injectable Solution subcutaneously once daily for 15 days at 0, 1, 3, and 5 mg/kg. There were 8 dogs (4 males and 4 females) in the 1 mg/kg group and 16 dogs (8 males and 8 females) in all other groups. The primary treatment-related findings were injection site reactions. Swelling, thickened skin, or pain at one or more of the injection sites on one or more days of the study were observed in 6 of 16 animals treated with 3 mg/kg/day and 5 of 16 animals treated with 5 mg/kg/day. Additionally, the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) was prolonged (67.5 seconds, reference range 9-15 seconds) in one male dog in the 1 mg/kg group on study day 15. Relationship of the prolonged APTT to drug administration could not be determined.
Beagle dogs approximately 8 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Injectable Solution subcutaneously once daily for 15 days at 0, 1, 3, and 5 mg/kg using a protocol similar to the previous study. A dose dependent increase in frequency and severity of bone marrow hypoplasia was observed histologically. One placebo-treated dog died on day 14 of the study and was diagnosed with suppurative pancreatitis and esophagitis. Interpretation of the study results is complicated by the health status of study animals. Dogs used in the study were weaned early, minimally acclimated to the test facility, and many of the dogs in the study tested positive for coccidia.
Beagle dogs approximately 10 weeks of age were administered either placebo tablets for 2 days, CERENIA Tablets at 8 mg/kg for 2 days, placebo (saline) subcutaneously (SC) for 5 days, CERENIA Injectable Solution at 1 mg/kg SC for 5 days, or CERENIA Tablets at 2 mg/kg for 5 days (8 dogs in each dose group). Mild pain associated with injection was noted in more dogs and lasted longer in dogs that received maropitant injections compared to saline. Males administered CERENIA at 8 mg/kg orally for 2 days had a decrease in food consumption. Body weight and food consumption were variable throughout the 4 week acclimatization period. Two dogs that received 8 mg/kg maropitant orally for 2 days were below the reference range for reticulocyte counts. Decreases in reticulocyte counts were also seen in 4 (of 8) placebo treated dogs (SC saline for 5 days). Hypocellular femoral bone marrow described as "minimal" was seen in 1 male that received 1 mg/kg maropitant SC for 5 days; reticulocyte counts were not available for this dog.
Twenty four Beagle dogs approximately 16 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Injectable Solution intravenously once daily for 5 days at 0, 1, and 3 mg/kg (4 females and 4 males per group). CERENIA Injectable Solution was administered at room temperature over 1-2 minutes. Reaction to injection was not specifically recorded. One male dog in the 1 mg/kg group had low hematocrit and white blood cell count on study day 5. One female dog in the 3 mg/kg group had an increased fibrinogen on study day 5. There were no other clinically relevant findings during the study, at necropsy or in histopathology.
Thirty-two domestic short hair cats (16 males and 16 females) approximately 16 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Injectable Solution subcutaneously once daily for 15 days at 0, 1, 3, and 5 mg/kg. There were 8 cats (4 males and 4 females) in each group. Treatment-related, dose dependent findings included pain associated with injection of CERENIA and injection site heat, pain, redness, and firmness. Pain on injection was observed in 5% of cats at 0 mg/kg, 50% of cats at 1 mg/kg, and 75% of cats at 3 and 5 mg/kg. Injection site firmness >10 mm in diameter was observed at one or more of the injection sites, on one or more days of the study, in 1 of 8 cats at 1 mg/kg, 7 of 8 cats at 3 mg/kg, and 7 of 8 cats at 5 mg/kg. There was a statistically significant reduction (p=0.0171) in food intake at 5 mg/kg compared to cats at 0 mg/kg. One cat at 5 mg/kg was lethargic on Days 12, 13, and 14 of the study. Increased skin turgor was observed in 1 cat at 3 mg/kg on Days 10 and 11, 1 cat at 3 mg/kg on Day 12, and 1 cat at 5 mg/kg on Day 12. At gross necropsy, there were no treatment-related findings. Histopathologic evaluation of injection sites revealed a dose dependent inflammatory response.
Twenty-four healthy domestic shorthair cats (12 males and 12 females) approximately 16 weeks of age were administered maropitant at 1 or 3 mg/kg, or saline at 0.1 mL/kg intravenously once daily for 5 days. CERENIA Injectable Solution was administered at room temperature over 1-2 minutes. Reaction to injection was not specifically recorded, but one cat experienced discomfort with accidental extravascular administration. There were no clinically relevant findings during the study, at necropsy or in histopathology.
STORAGE CONDITIONS
CERENIA Injectable Solution should be stored at controlled room temperature 20-25°C (68-77°F) with excursions between 15-30°C (59-86°F). After first vial puncture, CERENIA Injectable Solution should be stored at refrigerated temperature 2-8°C (36-46°F). Use within 90 days of first vial puncture. Stopper may be punctured a maximum of 25 times.
HOW SUPPLIED
CERENIA Injectable Solution is supplied in 20 mL amber glass vials. Each mL contains 10 mg of maropitant as maropitant citrate.
NADA #141-263, Approved by FDA
1. Diemunsch P, Grelot L. Potential of substance P antagonists as antiemetics. [Review] [60 refs]. Drugs. 2000;60:533-46.
NADA #141-263, Approved by FDA
Kalamazoo, MI 49007
Revised: October 2015 Made in France
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mL Vial Carton Made in France
10 mg of maropitant/mL
For subcutaneous injection in
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law
restricts this drug to use by or
on the order of a licensed
NET CONTENTS: 20 mL
NADA #141-263, Approved by FDA

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mL Vial Carton Made in Brazil
Cerenia
Generic Name: maropitant citrate
Dosage Form: FOR ANIMAL USE ONLY
For oral use in dogs only
Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Cerenia Description
Maropitant is a neurokinin (NK 1 ) receptor antagonist that blocks the pharmacological action of substance P in the central nervous system (CNS). Maropitant is the non-proprietary designation for a substituted quinuclidine. The empirical formula is C 32 H 40 N 2 O C 6 H 8 O 7 H 2 O and the molecular weight 678.81. The chemical name is (2 S ,3 S )-2-benzhydryl- N -(5- tert -butyl-2-methoxybenzyl) quinuclidin-3-amine citrate monohydrate. Each peach-colored oval tablet is scored and contains 16, 24, 60 or 160 mg of maropitant as maropitant citrate per tablet.
The chemical structure of maropitant citrate is:
INDICATIONS
Cerenia (maropitant citrate) Tablets are indicated for the prevention of acute vomiting and the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs.
Cerenia Dosage and Administration
Cerenia Tablets are recommended for use in dogs 16 weeks and older.
For Prevention of Acute Vomiting
Administer Cerenia Tablets orally at a minimum dose of 2 mg/kg (0.9 mg/lb) body weight once daily for up to 5 consecutive days.
Cerenia Tablets may be used interchangeably with Cerenia Injectable Solution for once daily dosing for the prevention of acute vomiting.
For Prevention of Vomiting Due to Motion Sickness
Administer Cerenia Tablets orally at a minimum dose of 8 mg/kg (3.6 mg/lb) body weight once daily for up to 2 consecutive days. Dogs should be fasted 1 hour prior to administration of Cerenia Tablets. Administer Cerenia Tablets 2 hours prior to travel.
Not for use in humans. Keep out of the reach of children. In case of accidental ingestion, seek medical advice. Topical exposure may elicit localized allergic skin reactions in some individuals. Repeated or prolonged exposure may lead to skin sensitization. Wash hands with soap and water after administering drug. Cerenia is also an ocular irritant. In case of accidental eye exposure, flush with water for 15 minutes and seek medical attention.
In puppies younger than 11 weeks of age, histological evidence of bone marrow hypoplasia was seen at higher frequency and greater severity in puppies treated with Cerenia than in control puppies. In puppies 16 weeks and older, bone marrow hypoplasia was not seen (See Animal Safety Section).
Precautions
The safe use of Cerenia Tablets has not been evaluated in dogs used for breeding, pregnant or lactating bitches, dogs with gastrointestinal obstruction, or dogs that have ingested toxins. Use with caution in dogs with hepatic dysfunction. Use with caution with other medications that are highly protein bound. The concomitant use of Cerenia with other protein bound drugs has not been studied in dogs. Commonly used protein bound drugs include NSAIDs, cardiac, anticonvulsant and behavioral medications. The influence of concomitant drugs that may inhibit metabolism of Cerenia has not been evaluated. Drug compatibility should be monitored in patients requiring adjunctive therapy.
Adverse Reactions
Prevention of Acute Vomiting (minimum of 2 mg/kg)
The following adverse reactions were reported during the course of a US field study for the prevention of acute vomiting in dogs treated with Cerenia Tablets at a minimum of 2 mg/kg orally and/or Injectable Solution at 1.0 mg/kg subcutaneously once daily for up to 5 consecutive days:
Other clinical signs were reported but were <0.5% of dogs.
Prevention of Vomiting Due to Motion Sickness (minimum of 8 mg/kg)
The following adverse reactions were reported during US studies for the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs treated with Cerenia Tablets at a minimum of 8 mg/kg orally one time. Dogs may have experienced more than one of the observed adverse reactions.
The following adverse reactions were reported during a European field study for the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs treated with Cerenia Tablets at a minimum of 8 mg/kg orally once daily for 2 consecutive days. Dogs may have experienced more than one of the observed adverse reactions.
For a copy of the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) or to report adverse reactions call Pfizer Animal Health at 1-800-366-5288.
Cerenia - Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic characterization associated with maropitant after oral (PO) or subcutaneous (SC) administration in adult Beagle dogs is provided in the table below.
The absolute bioavailability of maropitant was much higher following SC injection (91% at 1 mg/kg) than after PO administration (24% at 2 mg/kg). Oral bioavailability may be underestimated due to the presence of nonlinear kinetics and the resulting longer T ½ seen after intravenous (IV) administration. Although hepatic first-pass metabolism contributed to the relatively low bioavailability after an oral dose, prandial status does not significantly affect the extent of oral bioavailability. Greater than dose-proportional drug exposure can be expected with an increase in dose (1-16 mg/kg PO). Systemic clearance of maropitant following IV administration was 970, 995, and 533 mL/hr/kg at doses of 1, 2 and 8 mg/kg, respectively. An accumulation ratio of 1.5 was observed following once-daily use of maropitant for five consecutive days at 1 mg/kg (SC) or 2 mg/kg (PO). Urinary recovery of maropitant and its major metabolite was minimal (<1% each). The hepatic metabolism of maropitant involves two cytochrome P-450 isoenzymes: CYP2D15 and CYP3A12. Based on in vitro enzyme kinetics data, it is believed that the non-linear kinetics may be partially associated with saturation of the low capacity enzyme (CYP2D15). However as doses increase (20-50 mg/kg PO), dose proportionality is re-established. Based upon in vitro enzyme kinetics, involvement of a high capacity enzyme (CYP3A12) may contribute to this return to dose linearity. Plasma protein binding of maropitant was high (99.5%).
Pharmacodynamics
Vomiting is a complex process coordinated centrally by the emetic center which consists of several brainstem nuclei (area postrema, nucleus tractus solitarius, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus) that receive and integrate sensory stimuli from central and peripheral sources and chemical stimuli from the circulation and the cerebro-spinal fluid. Maropitant is a neurokinin 1 (NK 1 ) receptor antagonist which acts by inhibiting the binding of substance P, a neuropeptide of the tachykinin family. Substance P is found in significant concentrations in the nuclei comprising the emetic center and is considered the key neurotransmitter involved in emesis.1 By inhibiting the binding of substance P within the emetic center, maropitant provides broad-spectrum effectiveness against neural (central) and humoral (peripheral) causes of vomiting. In vivo model studies in dogs have shown that maropitant has antiemetic effectiveness against both central and peripheral emetogens including apomorphine, and syrup of ipecac.
1 Diemunsch P, Grelot L. Potential of substance P antagonists as antiemetics. [Review] [60 refs]. Drugs. 2000;60:533-46.
EFFECTIVENESS
Prevention of Acute Vomiting
In laboratory model studies, Cerenia Tablets dosed at a minimum of 2 mg/kg BW reduced the number of emetic events associated with established neural (central) and humoral (peripheral) stimuli. Following administration of apomorphine (central emetic stimuli), vomiting was observed in 33% (4 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with Cerenia Tablets and 100% (12 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with placebo tablets. Following administration of syrup of ipecac (peripheral emetic stimuli) vomiting was observed in 33% (4 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with Cerenia Tablets and in 83% (10 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with placebo tablets.
In a study of 275 canine patients presented to veterinary hospitals with a history of acute vomiting, dogs were initially administered Cerenia Injectable Solution or placebo on Day 0. Following the initial dose, dogs allocated to the Cerenia group were treated with either Cerenia Tablets at a minimum of 2 mg/kg orally or Injectable Solution at 1 mg/kg subcutaneously once daily at the discretion of the clinician. Dogs allocated to the placebo group were treated using either an injectable placebo solution or placebo tablets once daily at the discretion of the clinician. Of the 199 dogs included in the analysis for effectiveness, 27 of 54 dogs (50%) in the placebo group displayed vomiting at some time during the study and 31 of 145 dogs (21.4%) in the treated group displayed vomiting during the study period.
Prevention of Vomiting due to Motion Sickness
In a study of canine veterinary patients taken on a one-hour car journey and treated with either Cerenia Tablets at a minimum dose of 8 mg/kg BW or placebo tablets 2 hours prior to the journey, 67 of 122 (55%) of dogs vomited during the journey when treated with placebo while 8 of 122 (7%) vomited during the journey after treatment with Cerenia Tablets. The probability that a dog in this study, prone to motion sickness would NOT vomit during a journey if treated with Cerenia Tablets was 93%, while the probability was 48% if treated with placebo.
ANIMAL SAFETY
Laboratory and field studies have demonstrated that Cerenia Tablets are well tolerated in dogs after oral administration.
Target Animal Safety Study for Acute Vomiting
Fifty six Beagle dogs (28 males and 28 females) approximately 16 weeks of age were administered Cerenia Tablets orally once daily for 15 days at 0, 2, 6, and 10 mg/kg. There were 8 dogs (4 males and 4 females) in the 2 mg/kg group and 16 dogs (8 males and 8 females) in all other groups. Cerenia Tablets caused decreases in food consumption and body weight that were not dose-dependent and did not persist after cessation of treatment.
Beagle dogs approximately 8 weeks of age were administered Cerenia Tablets orally once daily for 15 days at 0, 2, 6, and 10 mg/kg using a protocol similar to the previous study. A dose dependent increase in severity of bone marrow hypoplasia was observed histologically. Interpretation of these study results is complicated by the health status of study animals. Dogs used in the study were weaned early, minimally acclimated to the test facility, many of the dogs in the study tested positive for coccidia and some tested positive for canine parvovirus.
Target Animal Safety Study for Motion Sickness
Forty Beagle dogs (20 males and 20 females) between 16 – 18 weeks of age were administered Cerenia Tablets orally once daily for 6 days at 0, 8 and 24 mg/kg. There were 16 dogs (8 males and 8 females) in the 0 and 24 mg/kg groups and 8 dogs (4 males and 4 females) in the 8 mg/kg group. At 24 mg/kg, Cerenia Tablets caused decreases in food consumption, with decreases in body weight, liver and testis weight; and an increase in RBC count indicating hemoconcentration, but the effects on feed consumption, body weight, and RBCs did not persist in the post-treatment recovery period (beyond Day 5).
Beagle dogs approximately 8 weeks of age were administered Cerenia Tablets orally once daily for 6 days at 0, 8, and 24 mg/kg using a protocol similar to the previous study. One dog in the 24 mg/kg/day group died of unknown causes on study day 2 and a dose dependent increase in occurrence and severity of bone marrow hypoplasia and lymphoid depletion was observed histologically. Interpretation of these study results is complicated by the health status of study animals. Dogs used in the study were weaned early, minimally acclimated to the test facility, and many of the dogs in the study tested positive for coccidia. Additionally, some dogs in the study tested positive for canine parvovirus, however, clinical parvoviral disease was not definitively diagnosed.
Tolerance Study
Twenty four Beagle dogs (14 males and 10 females) between 11 and 25 weeks of age were administered Cerenia Tablets in 2 phases with 8 dogs per group. In the first phase the dogs were administered 0, 20 or 30 mg/kg orally once daily for 7 days and in the second phase 0, 40, or 50 mg/kg once daily for 7 days. Cerenia Tablets administered at 20 and 30 mg/kg caused occasional vomiting. Cerenia Tablets administered at 40 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg caused clinically relevant signs of weight loss, vomiting, soft stools, weakness, lethargy, salivation and hypokalemia. Additionally, leukopenia characterized by a neutropenia and a trend toward decreasing plasma phosphorus values was seen. Decreased heart rate and prolonged corrected QT intervals were seen in all treatment groups in a dose dependent manner.
In US field studies in veterinary patients, Cerenia Tablets and Injectable Solution were well tolerated in dogs presenting with various conditions including parvovirus, gastroenteritis, and renal disease. There were no notable differences in mean laboratory values between Cerenia-treated and placebo-treated patients.
Cerenia Tablets were used safely in dogs receiving other frequently used veterinary products such as fluid and electrolyte replacement solutions, antimicrobial agents, vaccines, antacids, and antiparasitic agents.
STORAGE CONDITIONS
Cerenia Tablets should be stored at controlled room temperature 20°–25°C (68°–77°F) with excursions between 15°–30°C (59°–86°F).
How is Cerenia Supplied
Cerenia peach-colored tablets are scored with a break line, and contain 16, 24, 60 or 160 mg of maropitant as maropitant citrate per tablet. Each tablet is marked with "MPT" and the tablet strength on one side and the Pfizer logo on the other. Each tablet size is packaged in blister packs containing 4 tablets per perforated sheet.
US Patents: See US 6,222,038; US 6,255,320
NADA #141-262, Approved by FDA

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 16 mg Tablets Carton
For oral use in dogs only
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use
by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
4 Tablets Per Blister Card
NADA #141-262, Approved by FDA

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 24 mg Tablets Carton
For oral use in dogs only
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use
by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
4 Tablets Per Blister Card
NADA #141-262, Approved by FDA

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 60 mg Tablets Carton
For oral use in dogs only
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use
by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
4 Tablets Per Blister Card
NADA #141-262, Approved by FDA

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 160 mg Tablets Carton
For oral use in dogs only
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use
by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
4 Tablets Per Blister Card
NADA #141-262, Approved by FDA

maropitant citrate tablet
maropitant citrate tablet
maropitant citrate tablet
maropitant citrate tablet
- Osmolex ER Osmolex ER (amantadine hydrochloride) is a proprietary formulation of immediate release and.
- Erleada Erleada (apalutamide) is an oral androgen receptor inhibitor for the treatment of men with.
- Symdeko Symdeko (ivacaftor / tezacaftor tablets and ivacaftor tablets) is a cystic fibrosis transmembrane.
- Dexycu Dexycu (dexamethasone) is a long-acting, injectable corticosteroid formulation administered.
Drugs.com Mobile Apps
The easiest way to lookup drug information, identify pills, check interactions and set up your own personal medication records. Available for Android and iOS devices.
About
Terms & Privacy
Subscribe to receive email notifications whenever new articles are published.
Drugs.com provides accurate and independent information on more than 24,000 prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines and natural products. This material is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Data sources include Micromedex® (updated Jan 31st, 2018), Cerner Multum™ (updated Feb 2nd, 2018), Wolters Kluwer™ (updated Feb 2nd, 2018) and others. To view content sources and attributions, please refer to our editorial policy.
We comply with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information - verify here
Cerenia (maropitant citrate) – Indlægsseddel - QA04AD90
Updated on site: 09-Feb-2018


Indhold af artikel

Cerenia tabletter til hunde
1. NAVN OG ADRESSE PÅ INDEHAVEREN AF MARKEDSFØRINGSTILLADELSEN SAMT PÅ DEN INDEHAVER AF VIRKSOMHEDSGODKENDELSE, SOM ER ANSVARLIG FOR BATCHFRIGIVELSE, HVIS FORSKELLIG HERFRA
Indehaver af markedsføringstilladelsen: Zoetis Belgium SA
Rue Laid Burniat 1 1348 Louvain-la-Neuve BELGIEN
Fremstiller ansvarlig for batchfrigivelse: FAREVA AMBOISE
29 route des Industries
37530 Pocé-sur-Cisse FRANKRIG
2. VETERINÆRLÆGEMIDLETS NAVN
Cerenia 16 mg tabletter til hunde
Cerenia 24 mg tabletter til hunde
Cerenia 60 mg tabletter til hunde
Cerenia 160 mg tabletter til hunde
3. ANGIVELSE AF DET AKTIVE STOF(FER) OG ANDRE INDHOLDSSTOFFER
Hver tablet indeholder 16 mg, 24 mg, 60 mg eller 160 mg maropitant som maropitant citrat monohydrat.
Tabletterne indeholder også Sunset Yellow (E110) som farvestof.
Tabletterne er svagt orange og har delekærv som gør, at tabletten kan deles i to halvdele. Hver tablet er mærket med bogstaverne ”MPT” og tal, der angiver mængden af maropitant på den ene side og glat på den anden side.
4. INDIKATIONER
• Til forebyggelse af kvalme forårsaget af kemoterapi.
• Til forebyggelse af opkastning forårsaget af transportsyge.
• Til forebyggelse og behandling af opkastning i forbindelse med behandling med Cerenia- injektionsvæske, opløsning og i kombination med anden støttebehandling.
5. KONTRAINDIKATIONER

6. BIVIRKNINGER
Hvis hunden får Cerenia på en fuldstændig tom mave, kan det fremkalde opkastning hos hunden. Hvis hunden får et let måltid eller en godbid inden dosering har det vist sig at hjælpe til at begrænse denne virkning.
Faste før dosering bør undgås.
Cerenia er ikke et beroligende middel og nogle hunde, som lider af transportsyge, kan vise tegn på kvalme under rejsen i form af savlen og døsighed. Disse symptomer er forbigående og ophører, når transporten er slut.
Kontakt din dyrlæge, hvis du observerer bivirkninger. Dette gælder også bivirkninger, der ikke allerede er anført i denne indlægsseddel eller hvis du mener, at dette lægemiddel ikke har virket efter anbefalingerne.
7. DYREARTER
8. DOSERING FOR HVER DYREART, ANVENDELSESMÅDE OG INDGIVELSESVEJ
Til oral anvendelse.
Til forebyggelse af kvalme forårsaget af kemoterapi og til behandling og forebyggelse af opkastning (undtagen transportsyge), kun til hunde, der er 8 uger eller ældre.
For at behandle eller forebygge opkastning, som ikke skyldes køre- eller søsyge, gives Cerenia tabletter en gang daglig med en dosis på 2 mg pr. kg. legemsvægt med det antal tabletter, som er angivet i nedenstående tabel. Tabletterne kan deles via delekærven på tabletten.
For at forebygge opkastning bør tabletterne gives mere end 1 time på forhånd. Virkningen varer ca. 24 timer, og derfor kan tabletterne gives aftenen før administrationen af et stof, der kan forårsage opkastning (f.eks. kemoterapi).
Cerenia kan bruges til at behandle eller forebygge opkastning, enten som tabletter eller som injektionsvæske, opløsning givet én gang dagligt. Cerenia injektionsvæske, opløsning kan gives i op til 5 dage og Cerenia tabletter i op til 14 dage.

Til forebyggelse af kvalme forårsaget af kemoterapi
Behandling og forebyggelse af opkastning (undtagen transportsyge)
Hundens vægt (kg)
* Til hunde under 3 kg kan præcis dosering ikke opnås.
Til forebyggelse af opkastning, forårsaget af køre- og søsyge, kun til hunde, der er 16 uger eller ældre.
For at forebygge opkastning forårsaget af køre- og søsyge gives Cerenia tabletter en gang daglig med en dosis på 8 mg maropitant pr. kg. legemsvægt med det antal tabletter, som er angivet i nedenstående tabel. Tabletter kan deles via delekærven på tabletten.
Tabletterne bør gives mindst én time før rejsens påbegyndelse. Den kvalmestillende effekt varer i mindst 12 timer, hvilket muliggør dosering aftenen før en tidlig afrejse. Behandling kan gentages i højst 2 på hinanden følgende dage.
Ved gentagen behandling kan lavere dosis end den anbefalede være tilstrækkeligt hos nogle hunde.
Forebyggelse af køre- og søsyge
Hundens vægt (kg)
9. OPLYSNINGER OM KORREKT ANVENDELSE
Tabletterne udtages fra blisterpakningen på følgende måde:
• Fold eller skær først langs den stiplede linie mellem hver tablet angivet ved saksesymbolet
• Find afrivningsslippen eller skær som vist ved pilesymbolet
• Mens der holdes fast på den ene side ved snittet, trækkes den anden side mod midten af blisterpakningen til tabletten kan ses.
• Fjern tabletten fra pakningen og giv tabletten som anvist.

OBS: Man bør ikke forsøge at trykke tabletten gennem bagsiden af blister pakningen, da dette både vil beskadige tabletten og blisterpakningen.
Mod transportsyge anbefales at give et let måltid eller en godbid før dosering. Lang faste inden administrationen bør undgås.
Cerenia tabletter bør ikke gives ”indpakket” i foder, da dette kan forsinke opløsningen af tabletten og dermed tidspunktet for tablettens virkning.
Hunden bør observeres omhyggeligt efter indgiften for at sikre, at hver tablet er slugt.
10. TILBAGEHOLDELSESTID
11. EVENTUELLE SÆRLIGE FORHOLDSREGLER VEDRØRENDE OPBEVARING
Opbevares utilgængeligt for børn.
Dette veterinærlægemiddel kræver ingen særlige forholdsregler vedrørende opbevaringen.
Halve tabletter bør højst opbevares i 2 dage efter de er trykket ud af blisterpakken. Ubrugte halve tabletter lægges tilbage i den åbnede blister og opbevares i æsken.
Brug ikke dette veterinærlægemiddel efter den udløbsdato, der står på blisterpakken efter EXP.
12. SÆRLIGE ADVARSLER
Særlige advarsler for hver dyreart :
Opkastninger kan skyldes alvorlige, stærkt svækkende lidelser og årsagen skal undersøges. Lægemidler som Cerenia bør bruges sammen med andre forholdsregler som kontrol med foderet og væsketerapi, som anbefalet af din dyrlæge. Maropitants sikkerhed ved behandling af målpopulationen (dvs. unge hunde der lider af viral enterititis) i mere end 5 dage er ikke undersøgt. Hvis det vurderes, at det er nødvendigt at behandle i mere en 5 dage, bør der iværksættes omhyggelig monitorering af potentielle bivirkninger.
Maropitant nedbrydes i leveren og skal derfor bruges med forsigtighed til patienter med leverlidelse. Da maropitant akkumuleres i kroppen under en 14-dages behandlingsperiode på grund af en metabolisk mætning, bør der ved langtidsbehandling iværksættes omhyggelig overvågning af leverfunktionen og bivirkninger.
Special forholdsregler til brug hos dyr:
Sikkerheden af det veterinærmedicinske lægemiddel er ikke undersøgt i hunde yngre end 16 uger for dosen 8 mg/kg (transportsyge), hos hunde yngre end 8 uger for dosen 2 mg/kg (opkastning) eller hos drægtige eller diegivende tæver. Den ansvarlige dyrlæge bør foretage en risikovurdering før brug af Cerenia til hunde under 8 respektive 16 uger eller til drægtige eller diegivende tæver.
Efter overdosering højere end 20 mg/kg er set spredte kliniske symptomer som opkastning efter første indgift, forøget spytsekretion og vandig afføring.
Særlige forholdsregler der skal træffes af personer, der administrerer lægemidlet til dyr :
Personer med kendt overfølsomhed over for maropitant bør administrere veterinærlægemidlet med forsigtighed.

Vask hænderne efter håndtering. I tilfælde af selvindgivelse ved hændeligt uheld skal der straks søges læge, og indlægssedlen eller etiketten bør vises til lægen.
13. EVENTUELLE SÆRLIGE FORHOLDSREGLER VED BORTSKAFFELSE AF UBRUGTE LÆGEMIDLER ELLER AFFALD FRA SÅDANNE, OM NØDVENDIGT
Kontakt din dyrlæge eller apotekspersonalet vedrørende bortskaffelse af lægemidler, der ikke længere findes anvendelse for. Disse foranstaltninger skal bidrage til at beskytte miljøet.
14. DATO FOR SENESTE GODKENDELSE AF INDLÆGSSEDLEN
Yderligere information om dette lægemiddel er tilgængelig på Det Europæiske Lægemiddelagenturs hjemmeside (http://www.ema.europa.eu).
15. ANDRE OPLYSNINGER
Cerenia tabletter findes i blisterpakninger med 4 tabletter i hver pakke.
Receptpligtig medicin oplistet. Producent: "Zoetis Belgium SA"
Du bedes kontakte den lokale repræsentant for indehaveren af markedsføringstilladelsen, hvis du ønsker yderligere oplysninger om dette lægemiddel.
Zoetis Belgium SA
Oriola Vilnius UAB
Tél/Tel.: +32 (0) 800 99 189
Tel: +370 610 05088
Zoetis Belgium SA
Zoetis Belgium SA
Teл: +359 2 4775791
Tél/Tel.: +352 8002 4026
Zoetis Česká republika, s.r.o.
Zoetis Hungary Kft.
Tel: +420 257 101 111
Tel: +361 224 5222
Orion Pharma Animal Health
Tlf: +45 86 14 00 00
Tel: +356 21 465 797
Zoetis Deutschland GmbH
Tel: +49 30 330063 0
Tel: +31 (0)10 714 0900
Oriola Vilnius UAB
Orion Pharma Animal Health
Tel: +370 610 05088
Tlf: +47 40 00 41 90
Zoetis Hellas S.A.
Zoetis Österreich GmbH
Τηλ.: +30 210 6791900
Tel: + 43 1 2701100 110
Zoetis Spain, S.L.
Zoetis Polska Sp. z o.o.
Tel: +34 91 4191900
Tel: +48 22 2234800
Zoetis Portugal, Lda.
Tél: +33 (0)810 734 937
Tel: +351 21 042 72 00
Zoetis B.V., Podružnica Zagreb za promidžbu
Zoetis România SRL
Tel: +385 1 644 1460
Tel: +40 21 202 3083
Zoetis Belgium SA
Zoetis B.V., Podružnica Zagreb za promidžbu
Tel: +353 (0) 1 256 9800
Tel: +385 1 644 1460
Zoetis Česká republika, s.r.o.
Sími: +354 540 80 00
Tel: +420 257 101 111
Zoetis Italia S.r.l.
Zoetis Finland Oy
Tel: +39 06 3366 8133
Puh/Tel: +358 (0)9 4300 40
Zoetis Hellas S.A.
Orion Pharma Animal Health
Τηλ.: +30 210 6791900
Tel: +46 (0)8 623 64 40
Oriola Vilnius UAB
Zoetis UK Limited
Tel: +370 610 05088
Tel: +44 (0) 845 300 8034

Cerenia 10 mg/ml injektionsvæske, opløsning til hunde og katte
1. NAVN OG ADRESSE PÅ INDEHAVEREN AF MARKEDSFØRINGSTILLADELSEN SAMT PÅ DEN INDEHAVER AF VIRKSOMHEDSGODKENDELSE, SOM ER ANSVARLIG FOR BATCHFRIGIVELSE, HVIS FORSKELLIG HERFRA
Indehaver af markedsføringstilladelsen: Zoetis Belgium SA
Rue Laid Burniat 1 1348 Louvain-la-Neuve BELGIEN
Fremstiller ansvarlig for batchfrigivelse: FAREVA AMBOISE
29 route des Industries
37530 Pocé-sur-Cisse FRANKRIG
2. VETERINÆRLÆGEMIDLETS NAVN
Cerenia 10 mg/ml injektionsvæske, opløsning til hunde og katte
3. ANGIVELSE AF DET AKTIVE STOF OG ANDRE INDHOLDSSTOFFER
Injektionsvæsken indeholder 10 mg maropitant pr. ml som maropitant citrat monohydrat, som en klar, farveløs til svagt gul opløsning.
Den indeholder også metakresol som konserveringsmiddel.
• Til behandling og forebyggelse af kvalme forårsaget af kemoterapi.
• Til forebyggelse af opkastning, undtagen opkastning forårsaget af transportsyge.
• Til forebyggelse og behandling af opkastning i kombination med anden veterinær- og støttende terapi.
• Til forebyggelse af perioperativ kvalme og opkastning samt forbedring af rekonvalescens efter universel anæstesi efter anvendelse af µ-opiatreceptoragonisten morphin.
• Til forebyggelse af opkastning og reduktion af kvalme, undtagen opkastning forårsaget af transportsyge.
• Til behandling af opkastning i kombination med anden støttende terapi.

Smerte på injektionsstedet kan forekomme under subkutan injektion.
Det er meget almindeligt at der hos katte observeres moderat til alvorligt respons over for injektion (hos cirka en tredjedel af kattene).
I meget sjældne tilfælde kan anafylaktiske reaktioner (allergisk ødem, urticaria, erytem, kollaps, dyspnø, blege slimhinder) forekomme.
Hyppigheden af bivirkninger er defineret som:
- Meget almindelig (flere end 1 ud af 10 behandlede dyr, der viser bivirkninger i løbet af en behandling)
- Almindelige (flere end 1, men færre end 10 dyr af 100 behandlede dyr)
- Ikke almindelige (flere end 1, men færre end 10 dyr af 1.000 behandlede dyr)
- Sjældne (flere end 1, men færre end 10 dyr ud af 10.000 behandlede dyr)
- Meget sjælden (færre end 1 dyr ud af 10.000 behandlede dyr, herunder isolerede rapporter).
Kontakt din dyrlæge, hvis du observerer bivirkninger. Dette gælder også bivirkninger, der ikke allerede er anført i denne indlægsseddel eller hvis du mener, at dette lægemiddel ikke har virket efter anbefalingerne.
8. DOSERING FOR HVER DYREART, ANVENDELSESMÅDE OG INDGIVELSESVEJ
Til subkutan eller intravenøs injektion hos hunde og katte.
Cerenia injektionsvæske, opløsning skal injiceres subkutant eller intravenøst, en gang daglig med en dosis på 1 mg pr. kg legemsvægt (1 ml pr.10 kg legemsvægt). Behandlingen kan gentages i op til fem på hinanden følgende dage. Ved intravenøs anvendelse Cerenia bør gives som en enkelt bolus uden at blande produktet med andre væsker.
Hos hunde kan Cerenia bruges til at behandle eller forebygge opkastning en gang daglig i op til 5 dage.
9. OPLYSNINGER OM KORREKT ANVENDELSE
For at forebygge opkastning bør Cerenia gives mere end 1 time på forhånd. Varigheden af effekten er omkring 24 timer og derfor kan behandlingen gives aftenen før behandlingen med et brækningsfremkaldende middel, f.eks. kemoterapi.
På grund af den hyppige forekomst af forbigående smerte under subkutan injektion, skal dyret eventuelt fastholdes på en passende måde. Smerte ved injektion kan reduceres ved at produktet injiceres i kold tilstand.

11. EVENTUELLE SÆRLIGE FORHOLDSREGLER VEDRØRENDE OPBEVARING
Opbevares utilgængeligt for børn.
Dette veterinærlægemiddel kræver ingen særlige forholdsregler vedrørende opbevaringen. Opbevaringstid efter åbning af hætteglasset: 28 dage.
Brug ikke dette veterinærlægemiddel efter den udløbsdato, der står på hætteglassets etiket efter EXP.
12. SÆRLIGE ADVARSLER
Særlige advarsler for hver dyreart :
Opkastninger kan skyldes alvorlige, stærkt svækkende lidelser og årsagen skal undersøges. Lægemidler som Cerenia bør bruges sammen med andre forholdsregler som kontrol med foderet og væsketerapi, som anbefalet af din dyrlæge.
Maropitant nedbrydes i leveren og skal derfor bruges med forsigtighed til patienter med leverlidelse. Cerenia bør bruges med forsigtighed til dyr, der lider af, eller er prædisponerede for hjertelidelser
Brug af Cerenia-injektionsvæske, opløsning mod opkastning forårsaget af køresyge anbefales ikke.
Cerenias reducerende virkning på kvalme blev vist i studier, hvor der blev anvendt en model (kvalme forårsaget af xylazin).
Special forholdsregler til brug hos dyr:
Sikkerheden af Cerenia er ikke undersøgt i hunde yngre end 8 uger eller hos katte yngre end 16 uger og hos drægtige eller diegivende hunde og katte. Den ansvarlige dyrlæge bør foretage en risikovurdering før brug af Cerenia til hunde under 8 uger, hos katte mindre end 16 uger eller til drægtige eller diegivende katte og hunde.
Særlige forholdsregler der skal træffes af personer, der administrerer lægemidlet til dyr :
Personer med kendt overfølsomhed over for maropitant bør administrere veterinærlægemidlet med forsigtighed.
Vask hænderne efter håndtering. I tilfælde af selvindgivelse ved hændeligt uheld skal der straks søges læge, og indlægssedlen eller etiketten bør vises til lægen. Maropitant har vist sig at være et muligt øjenirriterende stof. I tilfælde af at stoffet ved et uheld kommer i øjet, skyl øjet med masser af vand og der søges læge.
Drægtighed og laktation:
Må kun bruges efter risikovurdering af den ansvarlige dyrlæge, da der for ingen dyrearters vedkommende er gennemført konklusive reproduktionstoksikologiske undersøgelser.
Interaktion med andre lægemidler og andre former for interaktion:
Cerenia bør ikke bruges samtidig med Ca-kanal antagonister, da maropitant har affinitet til Ca- kanaler.
Maropitant er stærkt bundet til plasmaproteiner og kan konkurrere med andre stærkt bundne stoffer.
Overdosis (symptomer, nødforanstaltninger, modgift):
Bortset fra forbigående reaktioner ved injektionsstedet under subkutan injektion, var Cerenia veltålt af hunde og unge katte, der fik daglige injektioner med Cerenia injektionsvæske, opløsning op til 5 mg/kg (5 gange den anbefalede dosis) i 15 på hinanden følgende dage (3 gange den anbefalede doseringsvarighed). Der er ikke blevet udarbejdet data for overdoseringer hos voksne katte.

Da der ikke er foretaget forligelighedsstudier, må dette veterinære lægemiddel ikke blandes med andre veterinære lægemidler i samme sprøjte.
13. EVENTUELLE SÆRLIGE FORHOLDSREGLER VED BORTSKAFFELSE AF UBRUGTE LÆGEMIDLER ELLER AFFALD FRA SÅDANNE, OM NØDVENDIGT
Kontakt din dyrlæge eller apotekspersonalet vedrørende bortskaffelse af lægemidler, der ikke længere findes anvendelse for. Disse foranstaltninger skal bidrage til at beskytte miljøet.
14. DATO FOR SENESTE GODKENDELSE AF INDLÆGSSEDLEN
Yderligere information om dette lægemiddel er tilgængelig på Det Europæiske Lægemiddelagenturs hjemmeside (http://www.ema.europa.eu).
15. ANDRE OPLYSNINGER
Receptpligtig medicin oplistet:
Cerenia 10 mg/ml injektionsvæske, opløsning til hunde og katte findes i 20 ml ravfarvet hætteglas. Hver æske indeholder 1 hætteglas.
Du bedes kontakte den lokale repræsentant for indehaveren af markedsføringstilladelsen, hvis du ønsker yderligere oplysninger om dette lægemiddel.
Zoetis Belgium SA
Oriola Vilnius UAB
Tél/Tel.: +32 (0) 800 99 189
Tel: +370 610 05088
Zoetis Belgium SA
Zoetis Belgium SA
Teл: +359 2 4775791
Tél/Tel.: +352 8002 4026
Zoetis Česká republika, s.r.o.
Zoetis Hungary Kft.
Tel: +420 257 101 111
Tel: +361 224 5222
Orion Pharma Animal Health
Tlf: +45 86 14 00 00
Tel: +356 21 465 797
Zoetis Deutschland GmbH
Tel: +49 30 330063 0
Tel: +31 (0)10 714 0900
Oriola Vilnius UAB
Orion Pharma Animal Health
Tel: +370 610 05088
Tlf: +47 40 00 41 90
Zoetis Hellas S.A.
Zoetis Österreich GmbH
Τηλ.: +30 210 6791900
Tel: + 43 1 2701100 110
Zoetis Spain, S.L.
Zoetis Polska Sp. z o.o.
Tel: +34 91 4191900
Tel: +48 22 2234800
Zoetis Portugal, Lda.
Tél: +33 (0)810 734 937
Tel: +351 21 042 72 00
Zoetis B.V., Podružnica Zagreb za promidžbu
Zoetis România SRL
Tel: +385 1 644 1460
Tel: +40 21 202 3083
Zoetis Belgium SA
Zoetis B.V., Podružnica Zagreb za promidžbu
Tel: +353 (0) 1 256 9800
Tel: +385 1 644 1460
Zoetis Česká republika, s.r.o.
Sími: +354 540 80 00
Tel: +420 257 101 111
Zoetis Italia S.r.l.
Zoetis Finland Oy
Tel: +39 06 3366 8133
Puh/Tel: +358 (0)9 4300 40
Zoetis Hellas S.A.
Orion Pharma Animal Health
Τηλ.: +30 210 6791900
Tel: +46 (0)8 623 64 40
Oriola Vilnius UAB
Zoetis UK Limited
Tel: +370 610 05088
Tel: +44 (0) 845 300 8034
Kommentarer








Vetxed.com med hjælp fra:
Vi bruger cookies for at kunne arbejde effektivt. Du godkender dette ved at bruge denne hjemmeside. Godkend brugen af cookies.
Cerenia Tablets
The information provided typically includes the following:
- Cerenia Tablets Indications
- Warnings and cautions for Cerenia Tablets
- Direction and dosage information for Cerenia Tablets
Cerenia Tablets
For oral use in dogs only
Cerenia Tablets Caution
Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Description
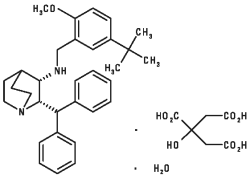
Maropitant is a neurokinin (NK1) receptor antagonist that blocks the pharmacological action of substance P in the central nervous system (CNS). Maropitant is the non-proprietary designation for a substituted quinuclidine. The empirical formula is C32H40N2O C6H8O7 H2O and the molecular weight 678.81. The chemical name is (2S,3S)-2-benzhydryl-N-(5-tert-butyl-2-methoxybenzyl) quinuclidin-3-amine citrate monohydrate. Each peach-colored oval tablet is scored and contains 16, 24, 60 or 160 mg of maropitant as maropitant citrate per tablet.
The chemical structure of maropitant citrate is:
Cerenia Tablets Indications
CERENIA (maropitant citrate) Tablets are indicated for the prevention of acute vomiting and the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs.
Dosage and Administration
For Prevention of Acute Vomiting
For Prevention of Acute Vomiting in dogs 2-7 months of age: Administer CERENIA Tablets orally at a minimum dose of 2 mg/kg (0.9 mg/lb) body weight once daily for up to 5 consecutive days (see WARNINGS and Animal Safety).
For Prevention of Acute Vomiting in dogs 7 months of age and older: Administer CERENIA Tablets orally at a minimum dose of 2 mg/kg (0.9 mg/lb) body weight once daily until resolution of acute vomiting.
If vomiting persists despite treatment, the case should be re-evaluated. CERENIA is most effective in preventing acute vomiting associated with chemotherapy if administered prior to the chemotherapeutic agent.
For prevention of acute vomiting, dispense whole or half tablets in strength(s) that most closely result in a 2 mg/kg dose:
Dog body weight
Number of Tablets
Interchangeable use with CERENIA Injectable Solution for Prevention of Acute Vomiting:
In dogs that are actively vomiting, to ensure that the full initial dose is administered, CERENIA Injectable Solution is recommended at a dose of 1 mg/kg once daily. (See package insert for CERENIA injectable solution.) Thereafter, for the prevention of acute vomiting, CERENIA Tablets at a dose of 2 mg/kg once daily may be used interchangeably with CERENIA Injectable Solution for up to 5 days.
For Prevention of Vomiting Due to Motion Sickness in dogs 4 months and older
Administer CERENIA Tablets orally at a minimum dose of 8 mg/kg (3.6 mg/lb) body weight once daily for up to 2 consecutive days (see WARNINGS and Animal Safety).
Administer CERENIA Tablets a minimum of two hours prior to travel with a small amount of food to mitigate vomiting associated with administration of the dose on an empty stomach; however, refrain from feeding a full meal prior to travel.
Prevention of Vomiting Due to Motion Sickness in Dogs 4 months of age and older:
Dispense whole or half tablets in strengths that most closely result in an 8 mg/kg dose once daily for up to 2 consecutive days:
Dog body weight
Number of Tablets
CERENIA injectable solution should not be used interchangeably with CERENIA tablets for the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness (8mg/kg).
In puppies younger than 11 weeks of age, histological evidence of bone marrow hypocellularity was observed at higher frequency and greater severity in puppies treated with CERENIA compared to control puppies. In puppies 16 weeks and older, bone marrow hypocellularity was not observed (see ANIMAL SAFETY).
Precautions
The safe use of CERENIA has not been evaluated in dogs with gastrointestinal obstruction, or dogs that have ingested toxins.
Use with caution in dogs with hepatic dysfunction because CERENIA is metabolized by CYP3A enzymes (see Pharmacokinetics). Use with caution with other medications that are highly protein bound. The concomitant use of CERENIA with other protein bound drugs has not been studied in dogs. Commonly used protein bound drugs include NSAIDs, cardiac, anticonvulsant, and behavioral medications. The influence of concomitant drugs that may inhibit the metabolism of CERENIA has not been evaluated. Drug compatibility should be monitored in patients requiring adjunctive therapy.
CERENIA causes dose related decreases in appetite and body weight (see ANIMAL SAFETY). To maximize therapeutic potential of CERENIA, the underlying cause of vomiting should be identified and addressed in dogs receiving CERENIA.
Adverse Reactions
Prevention of Acute Vomiting (minimum of 2 mg/kg)
The following adverse reactions were reported during the course of a US field study for the prevention of acute vomiting in dogs treated with CERENIA Tablets at a minimum of 2 mg/kg orally and/or Injectable Solution at 1 mg/kg subcutaneously once daily for up to 5 consecutive days:
Frequency of Adverse Reactions by Treatment
Death during study
Euthanized during study
Other clinical signs were reported but were <0.5% of dogs.
Prevention of Vomiting Due to Motion Sickness (minimum of 8 mg/kg)
The following adverse reactions were reported during US studies for the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs treated with CERENIA Tablets at a minimum of 8 mg/kg orally one time. Dogs may have experienced more than one of the observed adverse reactions.
Frequency of Adverse Reactions by Treatment
1 Not associated with motion sickness
The following adverse reactions were reported during a European field study for the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs treated with CERENIA Tablets at a minimum of 8 mg/kg orally once daily for 2 consecutive days. Dogs may have experienced more than one of the observed adverse reactions.
Frequency of Adverse Reactions by Treatment
The following Adverse Reactions were reported during the conduct of a US clinical field trial where CERENIA Tablets were administered once daily for 28 consecutive days to 32 dogs: lethargy, vomiting, inappetence, corneal edema, and enlarged lymph nodes.
The following adverse events are based on post-approval adverse drug experience reporting. Not all adverse events are reported to FDA CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using these data.
The following adverse events are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency in dogs: depression/lethargy, anorexia, hypersalivation, vomiting, diarrhea, ataxia, and trembling.
Cases of ineffectiveness have been reported.
To report suspected adverse events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the SDS, contact Zoetis Inc. at 1-888-963-8471 or www.zoetis.com.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or online at http://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/SafetyHealth.
Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
Mean (±SD) Plasma Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Maropitant in Beagle Dogs after single dose and repeat oral doses of Maropitant:
2 mg/kg Single Dose
2 mg/kg repeat Doses 1
8 mg/kg Single Dose
8 mg/kg repeat Doses 1
1 Following once daily doses of maropitant for 14 days.
3 Ratio=Multiple Dose AUC(0-24)/Single Dose AUC(0-24), Least square means (95% Confidence Interval)
NA= Not Applicable
NC= Not Calculated
Following oral administration, median time to reach Cmax was within 2.5 hr. The absolute bioavailability of maropitant was low (24%) following oral administration of 2 mg/kg maropitant. After an oral dose, prandial status does not significantly affect the extent of oral bioavailability. Greater than dose-proportional drug exposure can be expected with an increase in dose (1-16 mg/kg PO). However as doses increase (20-50 mg/kg PO), the dose proportionality is re-established. Based upon in vitro enzyme kinetics, involvement of a high capacity enzyme (CYP3A12) may contribute to this return to dose linearity. Due to dose dependent pharmacokinetics, the maropitant concentrations reached steady state approximately after 4 and 8 days following 2 and 8 mg/kg, respectively. The observed drug accumulation ratios were 2.46 and 4.81, after oral administration of 2 and 8 mg/kg, respectively. The exposure of 10 week old puppies to maropitant was lower than that observed in adult dogs, particularly after repeat doses of 1 or 2 mg/kg. Systemic clearance of maropitant following IV administration was 970, 995, and 533 mL/hr/kg at doses of 1, 2 and 8 mg/kg, respectively.
Urinary recovery of maropitant and its major metabolite was minimal (<1% each). The hepatic metabolism of maropitant involves two cytochrome P-450 isoenzymes: CYP2D15 and CYP3A12. In in vitro enzyme kinetics data suggest that the non-linear kinetics may be partially associated with saturation of the low capacity enzyme (CYP2D15). Plasma protein binding of maropitant was high (99.5%).
Vomiting is a complex process coordinated centrally by the emetic center which consists of several brainstem nuclei (area postrema, nucleus tractus solitarius, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus) that receive and integrate sensory stimuli from central and peripheral sources and chemical stimuli from the circulation and the cerebro-spinal fluid. Maropitant is a neurokininn 1 (NK1) receptor antagonist which acts by inhibiting the binding of substance P, a neuropeptide of the tachykinin family. Substance P is found in significant concentrations in the nuclei comprising the emetic center and is considered the key neurotransmitter involved in emesis. 1 By inhibiting the binding of substance P within the emetic center, maropitant provides broad-spectrum effectiveness against neural (central) and humoral (peripheral) causes of vomiting. In vivo model studies in dogs have shown that maropitant has antiemetic effectiveness against both central and peripheral emetogens including apomorphine, and syrup of ipecac.
1 Diemunsch P, Grelot L. Potential of substance P antagonists as antiemetics. [Review] [60 refs]. Drugs. 2000;60:533-46.
Effectiveness
Prevention of Acute Vomiting
In laboratory model studies, CERENIA Tablets dosed at a minimum of 2 mg/kg BW reduced the number of emetic events associated with established neural (central) and humoral (peripheral) stimuli. Following administration of apomorphine (central emetic stimuli), vomiting was observed in 33% (4 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with CERENIA Tablets and 100% (12 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with placebo tablets. Following administration of syrup of ipecac (peripheral emetic stimuli) vomiting was observed in 33% (4 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with CERENIA Tablets and in 83% (10 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with placebo tablets.
In a study of 275 canine patients presented to veterinary hospitals with a history of acute vomiting, dogs were initially administered CERENIA Injectable Solution or placebo on Day 0. Following the initial dose, dogs allocated to the CERENIA group were treated with either CERENIA Tablets at a minimum of 2 mg/kg orally or Injectable Solution at 1 mg/kg subcutaneously once daily at the discretion of the clinician. Dogs allocated to the placebo group were treated using either an injectable placebo solution or placebo tablets once daily at the discretion of the clinician. Of the 199 dogs included in the analysis for effectiveness, 27 of 54 dogs (50%) in the placebo group displayed vomiting at some time during the study and 31 of 145 dogs (21.4%) in the treated group displayed vomiting during the study period.
Percent Of Vomiting For Each Study Day, Based Upon Treatment And Route Of Administration.
*2 dogs administered CERENIA were not observed on Day 0. Their vomiting status was unknown. 143 was used in the denominator for % vomited.
In US field studies in veterinary patients, CERENIA Tablets and Injectable Solution were well tolerated in dogs presenting with various conditions including parvovirus, gastroenteritis, and renal disease. There were no notable differences in mean laboratory values between CERENIA-treated and placebo-treated patients.
CERENIA Tablets were used safely in dogs receiving other frequently used veterinary products such as fluid and electrolyte replacement solutions, antimicrobial agents, vaccines, antacids, and antiparasitic agents.
Prevention of Vomiting due to Motion Sickness
In a study of canine veterinary patients taken on a one-hour car journey and treated with either CERENIA Tablets at a minimum dose of 8 mg/kg BW or placebo tablets 2 hours prior to the journey, 67 of 122 (55%) of dogs vomited during the journey when treated with placebo while 8 of 122 (7%) vomited during the journey after treatment with CERENIA Tablets. The probability that a dog in this study, prone to motion sickness would NOT vomit during a journey if treated with CERENIA Tablets was 93%, while the probability was 48% if treated with placebo.
ANIMAL SAFETY: Laboratory and field studies have demonstrated that CERENIA Tablets are well tolerated in dogs after oral administration.
Target Animal Safety Study for Acute Vomiting
Fifty six Beagle dogs (28 males and 28 females) approximately 16 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Tablets orally once daily for 15 days at 0, 2, 6, and 10 mg/kg. There were 8 dogs (4 males and 4 females) in the 2 mg/kg group and 16 dogs (8 males and 8 females) in all other groups. CERENIA Tablets caused decreases in food consumption and body weight that were not dose-dependent and did not persist after cessation of treatment.
Beagle dogs approximately 8 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Tablets orally once daily for 15 days at 0, 2, 6, and 10 mg/kg using a protocol similar to the previous study. A dose dependent increase in severity of bone marrow hypoplasia was observed histologically. Interpretation of these study results is complicated by the health status of study animals. Dogs used in the study were weaned early, minimally acclimated to the test facility, many of the dogs in the study tested positive for coccidia and some tested positive for canine parvovirus.
Beagle dogs approximately 10 weeks of age were administered either placebo tablets for 2 days, CERENIA Tablets at 8 mg/kg for 2 days, placebo (saline) subcutaneously (SC) for 5 days, CERENIA Injectable Solution at 1 mg/kg SC for 5 days, or CERENIA Tablets at 2 mg/kg for 5 days (8 dogs in each dose group). Mild pain associated with injection was noted in more dogs and lasted longer in dogs that received maropitant injections compared to saline. Males administered CERENIA at 8 mg/kg orally for 2 days had a decrease in food consumption. Body weight and food consumption were variable throughout the 4 week acclimation period. Two dogs that received 8 mg/kg maropitant orally for 2 days were below the reference range for reticulocyte counts. Decreases in reticulocyte counts were also seen in 4 (of 8) placebo treated dogs (SC saline for 5 days). Hypocellular femoral bone marrow described as “minimal” was seen in 1 male that received 1 mg/kg maropitant SC for 5 days; reticulocyte counts were not available for this dog.
Twenty four Beagle dogs (12 males and 12 females) 7 months of age were administered maropitant at doses of 0, 1, 5, and 20 mg/kg orally once daily for 93 consecutive days. Maropitant produced sporadic clinical signs (salivation, emesis), body weight loss, and lower serum albumin levels at 20 mg/kg/day. Maropitant increased P-R interval, P wave duration, and QRS amplitude in the 20 mg/kg /day dose group. One female in the 20 mg/kg/day group had increased cellularity of the bone marrow. This female was noted to have lower mean red cell parameters (red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit) and higher platelet counts and reticulocytes.
Target Animal Safety Study for Motion Sickness
Forty Beagle dogs (20 males and 20 females) between 16 - 18 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Tablets orally once daily for 6 days at 0, 8 and 24 mg/kg. There were 16 dogs (8 males and 8 females) in the 0 and 24 mg/kg groups and 8 dogs (4 males and 4 females) in the 8 mg/kg group. At 24 mg/kg, CERENIA Tablets caused decreases in food consumption, with decreases in body weight, liver and testis weight; and an increase in RBC count indicating hemoconcentration, but the effects on feed consumption, body weight, and RBCs did not persist in the post-treatment recovery period (beyond Day 5).
Beagle dogs approximately 8 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Tablets orally once daily for 6 days at 0, 8, and 24 mg/kg using a protocol similar to the previous study. One dog in the 24 mg/kg/day group died of unknown causes on study day 2 and a dose dependent increase in occurrence and severity of bone marrow hypoplasia and lymphoid depletion was observed histologically. Interpretation of these study results is complicated by the health status of study animals. Dogs used in the study were weaned early, minimally acclimated to the test facility, and many of the dogs in the study tested positive for coccidia. Additionally, some dogs in the study tested positive for canine parvovirus, however, clinical parvoviral disease was not definitively diagnosed.
Twenty four Beagle dogs (14 males and 10 females) between 11 and 25 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Tablets in 2 phases with 8 dogs per group. In the first phase the dogs were administered 0, 20 or 30 mg/kg orally once daily for 7 days and in the second phase 0, 40, or 50 mg/kg once daily for 7 days. CERENIA Tablets administered at 20 and 30 mg/kg caused occasional vomiting. CERENIA Tablets administered at 40 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg caused clinically relevant signs of weight loss, vomiting, soft stools, weakness, lethargy, salivation and hypokalemia. Additionally, leukopenia characterized by a neutropenia and a trend toward decreasing plasma phosphorus values was seen. Decreased heart rate and prolonged corrected QT intervals were seen in all treatment groups in a dose dependent manner.
Twenty-four Beagle dogs (12 males and 12 females) approximately 28 weeks of age were administered maropitant (mesylate salt) orally once daily for 90 days at 0, 1, 5, and 20 mg/kg. End of study body weights in the 20 mg/kg group were 8-15% lower than baseline body weights.
STORAGE CONDITIONS: CERENIA Tablets should be stored at controlled room temperature 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) with excursions between 15°-30°C (59°-86°F).
How Supplied
NADA #141-262, Approved by FDA
Manufactured by: Farvera, Amboise, France
Distributed by: Zoetis Inc., Kalamazoo, MI 49007
Revised: March 2016
333 PORTAGE STREET, KALAMAZOO, MI, 49007
Copyright © 2018 North American Compendiums. Updated: 2018-01-04
Drugs.com Mobile Apps
The easiest way to lookup drug information, identify pills, check interactions and set up your own personal medication records. Available for Android and iOS devices.
About
Terms & Privacy
Subscribe to receive email notifications whenever new articles are published.
Drugs.com provides accurate and independent information on more than 24,000 prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines and natural products. This material is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Data sources include Micromedex® (updated Jan 31st, 2018), Cerner Multum™ (updated Feb 2nd, 2018), Wolters Kluwer™ (updated Feb 2nd, 2018) and others. To view content sources and attributions, please refer to our editorial policy.
We comply with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information - verify here
Cerenia ®
For oral use in dogs only
Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
DESCRIPTION
Maropitant is a neurokinin (NK 1 ) receptor antagonist that blocks the pharmacological action of substance P in the central nervous system (CNS). Maropitant is the non-proprietary designation for a substituted quinuclidine. The empirical formula is C 32 H 40 N 2 O C 6 H 8 O 7 H 2 O and the molecular weight 678.81. The chemical name is (2 S ,3 S )-2-benzhydryl- N -(5- tert -butyl-2-methoxybenzyl) quinuclidin-3-amine citrate monohydrate. Each peach-colored oval tablet is scored and contains 16, 24, 60 or 160 mg of maropitant as maropitant citrate per tablet.
The chemical structure of maropitant citrate is:

INDICATIONS
CERENIA (maropitant citrate) Tablets are indicated for the prevention of acute vomiting and the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
For Prevention of Acute Vomiting
For Prevention of Acute Vomiting in dogs 2 -7 months of age: Administer CERENIA Tablets orally at a minimum dose of 2 mg/kg (0.9 mg/lb) body weight once daily for up to 5 consecutive days (see WARNINGS and Animal Safety).
For Prevention of Acute Vomiting in dogs 7 months of age and older: Administer CERENIA Tablets orally at a minimum dose of 2 mg/kg (0.9 mg/lb) body weight once daily until resolution of acute vomiting.
If vomiting persists despite treatment, the case should be re-evaluated. CERENIA is most effective in preventing acute vomiting associated with chemotherapy if administered prior to the chemotherapeutic agent.
For prevention of acute vomiting, dispense whole or half tablets in strength(s) that most closely result in a 2 mg/kg dose:
Interchangeable use with CERENIA Injectable Solution for Prevention of Acute Vomiting:
In dogs that are actively vomiting, to ensure that the full initial dose is administered, CERENIA Injectable Solution is recommended at a dose of 1 mg/kg once daily. (See package insert for CERENIA injectable solution.) Thereafter, for the prevention of acute vomiting, CERENIA Tablets at a dose of 2 mg/kg once daily may be used interchangeably with CERENIA Injectable Solution for up to 5 days.
For Prevention of Vomiting Due to Motion Sickness
For Prevention of Vomiting Due to Motion Sickness in dogs 4 months and older
For Prevention of Vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs 4 months of age and older: Administer CERENIA Tablets orally at a minimum dose of 8 mg/kg (3.6 mg/lb) body weight once daily for up to 2 consecutive days (see WARNINGS and Animal Safety).
Administer CERENIA Tablets a minimum of two hours prior to travel with a small amount of food to mitigate vomiting associated with administration of the dose on an empty stomach; however, refrain from feeding a full meal prior to travel.
Prevention of Vomiting Due to Motion Sickness in Dogs 4 months of age and older:
Dispense whole or half tablets in strengths that most closely result in an 8 mg/kg dose once daily for up to 2 consecutive days :
Dog body weight
Number of Tablets
CERENIA injectable solution should not be used interchangeably with CERENIA tablets for the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness (8mg/kg).
Not for use in humans. Keep out of the reach of children. In case of accidental ingestion, seek medical advice. Topical exposure may elicit localized allergic skin reactions in some individuals. Repeated or prolonged exposure may lead to skin sensitization. Wash hands with soap and water after administering drug. CERENIA is also an ocular irritant. In case of accidental eye exposure, flush with water for 15 minutes and seek medical attention.
In puppies younger than 11 weeks of age, histological evidence of bone marrow hypocellularity was observed at higher frequency and greater severity in puppies treated with CERENIA compared to control puppies. In puppies 16 weeks and older, bone marrow hypocellularity was not observed (see ANIMAL SAFETY ).
PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTIONS: The safe use of CERENIA Tablets has not been evaluated in dogs used for breeding, or in pregnant or lactating bitches.
The safe use of CERENIA has not been evaluated in dogs with gastrointestinal obstruction, or dogs that have ingested toxins.
Use with caution in dogs with hepatic dysfunction because CERENIA is metabolized by CYP3A enzymes (see Pharmacokinetics ). Use with caution with other medications that are highly protein bound. The concomitant use of CERENIA with other protein bound drugs has not been studied in dogs. Commonly used protein bound drugs include NSAIDs, cardiac, anticonvulsant, and behavioral medications. The influence of concomitant drugs that may inhibit the metabolism of CERENIA has not been evaluated. Drug compatibility should be monitored in patients requiring adjunctive therapy.
CERENIA causes dose related decreases in appetite and body weight (see ANIMAL SAFETY ). To maximize therapeutic potential of CERENIA, the underlying cause of vomiting should be identified and addressed in dogs receiving CERENIA.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Prevention of Acute Vomiting (minimum of 2 mg/kg)
The following adverse reactions were reported during the course of a US field study for the prevention of acute vomiting in dogs treated with CERENIA Tablets at a minimum of 2 mg/kg orally and/or Injectable Solution at 1 mg/kg subcutaneously once daily for up to 5 consecutive days:
Other clinical signs were reported but were <0.5% of dogs.
Prevention of Vomiting Due to Motion Sickness (minimum of 8 mg/kg)
The following adverse reactions were reported during US studies for the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs treated with CERENIA Tablets at a minimum of 8 mg/kg orally one time. Dogs may have experienced more than one of the observed adverse reactions.
Frequency of Adverse Reactions by Treatment
The following adverse reactions were reported during a European field study for the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs treated with CERENIA Tablets at a minimum of 8 mg/kg orally once daily for 2 consecutive days. Dogs may have experienced more than one of the observed adverse reactions.
Frequency of Adverse Reactions by Treatment
The following Adverse Reactions were reported during the conduct of a US clinical field trial where CERENIA Tablets were administered once daily for 28 consecutive days to 32 dogs: lethargy, vomiting, inappetence, corneal edema, and enlarged lymph nodes.
Post-Approval Experience
The following adverse events are based on post-approval adverse drug experience reporting. Not all adverse events are reported to FDA CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using these data.
The following adverse events are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency in dogs: depression/lethargy, anorexia, hypersalivation, vomiting, diarrhea, ataxia, and trembling.
Cases of ineffectiveness have been reported.
To report suspected adverse events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the SDS, contact Zoetis Inc. at 1-888-963-8471 or www.zoetis.com.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or online at http://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/SafetyHealth.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacokinetics
Mean (±SD) Plasma Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Maropitant in Beagle Dogs after single dose and repeat oral doses of Maropitant:
2 mg/kg repeat Doses1
Accumulation Ratio (Rac)3
1 Following once daily doses of maropitant for 14 days.
3 Ratio=Multiple Dose AUC(0-24)/Single Dose AUC(0-24), Least square means (95% Confidence Interval)
NA= Not Applicable
NC= Not Calculated
Following oral administration, median time to reach Cmax was within 2.5 hr. The absolute bioavailability of maropitant was low (24%) following oral administration of 2 mg/kg maropitant. After an oral dose, prandial status does not significantly affect the extent of oral bioavailability. Greater than dose-proportional drug exposure can be expected with an increase in dose (1-16 mg/kg PO). However as doses increase (20-50 mg/kg PO), the dose proportionality is re-established. Based upon in vitro enzyme kinetics, involvement of a high capacity enzyme (CYP3A12) may contribute to this return to dose linearity. Due to dose dependent pharmacokinetics, the maropitant concentrations reached steady state approximately after 4 and 8 days following 2 and 8 mg/kg, respectively. The observed drug accumulation ratios were 2.46 and 4.81, after oral administration of 2 and 8 mg/kg, respectively. The exposure of 10 week old puppies to maropitant was lower than that observed in adult dogs, particularly after repeat doses of 1 or 2 mg/kg. Systemic clearance of maropitant following IV administration was 970, 995, and 533 mL/hr/kg at doses of 1, 2 and 8 mg/kg, respectively.
Urinary recovery of maropitant and its major metabolite was minimal (<1% each). The hepatic metabolism of maropitant involves two cytochrome P-450 isoenzymes: CYP2D15 and CYP3A12. In in vitro enzyme kinetics data suggest that the non-linear kinetics may be partially associated with saturation of the low capacity enzyme (CYP2D15). Plasma protein binding of maropitant was high (99.5%).
Pharmacodynamics
Vomiting is a complex process coordinated centrally by the emetic center which consists of several brainstem nuclei (area postrema, nucleus tractus solitarius, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus) that receive and integrate sensory stimuli from central and peripheral sources and chemical stimuli from the circulation and the cerebro-spinal fluid. Maropitant is a neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonist which acts by inhibiting the binding of substance P, a neuropeptide of the tachykinin family. Substance P is found in significant concentrations in the nuclei comprising the emetic center and is considered the key neurotransmitter involved in emesis.1 By inhibiting the binding of substance P within the emetic center, maropitant provides broad-spectrum effectiveness against neural (central) and humoral (peripheral) causes of vomiting. In vivo model studies in dogs have shown that maropitant has antiemetic effectiveness against both central and peripheral emetogens including apomorphine, and syrup of ipecac.1Diemunsch P, Grelot L. Potential of substance P antagonists as antiemetics. [Review] [60 refs]. Drugs. 2000;60:533-46.
EFFECTIVENESS
Prevention of Acute Vomiting
In laboratory model studies, CERENIA Tablets dosed at a minimum of 2 mg/kg BW reduced the number of emetic events associated with established neural (central) and humoral (peripheral) stimuli. Following administration of apomorphine (central emetic stimuli), vomiting was observed in 33% (4 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with CERENIA Tablets and 100% (12 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with placebo tablets. Following administration of syrup of ipecac (peripheral emetic stimuli) vomiting was observed in 33% (4 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with CERENIA Tablets and in 83% (10 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with placebo tablets.
In a study of 275 canine patients presented to veterinary hospitals with a history of acute vomiting, dogs were initially administered CERENIA Injectable Solution or placebo on Day 0. Following the initial dose, dogs allocated to the CERENIA group were treated with either CERENIA Tablets at a minimum of 2 mg/kg orally or Injectable Solution at 1 mg/kg subcutaneously once daily at the discretion of the clinician. Dogs allocated to the placebo group were treated using either an injectable placebo solution or placebo tablets once daily at the discretion of the clinician. Of the 199 dogs included in the analysis for effectiveness, 27 of 54 dogs (50%) in the placebo group displayed vomiting at some time during the study and 31 of 145 dogs (21.4%) in the treated group displayed vomiting during the study period.
*2 dogs administered CERENIA were not observed on Day 0. Their vomiting status was unknown. 143 was used in the denominator for % vomited.
In US field studies in veterinary patients, CERENIA Tablets and Injectable Solution were well tolerated in dogs presenting with various conditions including parvovirus, gastroenteritis, and renal disease. There were no notable differences in mean laboratory values between CERENIA-treated and placebo-treated patients.
CERENIA Tablets were used safely in dogs receiving other frequently used veterinary products such as fluid and electrolyte replacement solutions, antimicrobial agents, vaccines, antacids, and antiparasitic agents
Prevention of Vomiting due to Motion Sickness
In a study of canine veterinary patients taken on a one-hour car journey and treated with either CERENIA Tablets at a minimum dose of 8 mg/kg BW or placebo tablets 2 hours prior to the journey, 67 of 122 (55%) of dogs vomited during the journey when treated with placebo while 8 of 122 (7%) vomited during the journey after treatment with CERENIA Tablets. The probability that a dog in this study, prone to motion sickness would NOT vomit during a journey if treated with CERENIA Tablets was 93%, while the probability was 48% if treated with placebo.
ANIMAL SAFETY
Laboratory and field studies have demonstrated that CERENIA Tablets are well tolerated in dogs after oral administration.
Target Animal Safety Study for Acute Vomiting
Fifty six Beagle dogs (28 males and 28 females) approximately 16 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Tablets orally once daily for 15 days at 0, 2, 6, and 10 mg/kg. There were 8 dogs (4 males and 4 females) in the 2 mg/kg group and 16 dogs (8 males and 8 females) in all other groups. CERENIA Tablets caused decreases in food consumption and body weight that were not dose-dependent and did not persist after cessation of treatment.
Beagle dogs approximately 8 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Tablets orally once daily for 15 days at 0, 2, 6, and 10 mg/kg using a protocol similar to the previous study. A dose dependent increase in severity of bone marrow hypoplasia was observed histologically. Interpretation of these study results is complicated by the health status of study animals. Dogs used in the study were weaned early, minimally acclimated to the test facility, many of the dogs in the study tested positive for coccidia and some tested positive for canine parvovirus.
Beagle dogs approximately 10 weeks of age were administered either placebo tablets for 2 days, CERENIA Tablets at 8 mg/kg for 2 days, placebo (saline) subcutaneously (SC) for 5 days, CERENIA Injectable Solution at 1 mg/kg SC for 5 days, or CERENIA Tablets at 2 mg/kg for 5 days (8 dogs in each dose group). Mild pain associated with injection was noted in more dogs and lasted longer in dogs that received maropitant injections compared to saline. Males administered CERENIA at 8 mg/kg orally for 2 days had a decrease in food consumption. Body weight and food consumption were variable throughout the 4 week acclimation period. Two dogs that received 8 mg/kg maropitant orally for 2 days were below the reference range for reticulocyte counts. Decreases in reticulocyte counts were also seen in 4 (of 8) placebo treated dogs (SC saline for 5 days). Hypocellular femoral bone marrow described as "minimal" was seen in 1 male that received 1 mg/kg maropitant SC for 5 days; reticulocyte counts were not available for this dog.
Twenty four Beagle dogs (12 males and 12 females) 7 months of age were administered maropitant at doses of 0, 1, 5, and 20 mg/kg orally once daily for 93 consecutive days. Maropitant produced sporadic clinical signs (salivation, emesis), body weight loss, and lower serum albumin levels at 20 mg/kg/day.
Maropitant increased P-R interval, P wave duration, and QRS amplitude in the 20 mg/kg /day dose group.
One female in the 20 mg/kg/day group had increased cellularity of the bone marrow. This female was noted to have lower mean red cell parameters (red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit) and higher platelet counts and reticulocytes.
Target Animal Safety Study for Motion Sickness
Forty Beagle dogs (20 males and 20 females) between 16 – 18 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Tablets orally once daily for 6 days at 0, 8 and 24 mg/kg. There were 16 dogs (8 males and 8 females) in the 0 and 24 mg/kg groups and 8 dogs (4 males and 4 females) in the 8 mg/kg group. At 24 mg/kg, CERENIA Tablets caused decreases in food consumption, with decreases in body weight, liver and testis weight; and an increase in RBC count indicating hemoconcentration, but the effects on feed consumption, body weight, and RBCs did not persist in the post-treatment recovery period (beyond Day 5).
Beagle dogs approximately 8 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Tablets orally once daily for 6 days at 0, 8, and 24 mg/kg using a protocol similar to the previous study. One dog in the 24 mg/kg/day group died of unknown causes on study day 2 and a dose dependent increase in occurrence and severity of bone marrow hypoplasia and lymphoid depletion was observed histologically. Interpretation of these study results is complicated by the health status of study animals. Dogs used in the study were weaned early, minimally acclimated to the test facility, and many of the dogs in the study tested positive for coccidia. Additionally, some dogs in the study tested positive for canine parvovirus, however, clinical parvoviral disease was not definitively diagnosed.
Tolerance Study
Twenty four Beagle dogs (14 males and 10 females) between 11 and 25 weeks of age were administered CERENIA Tablets in 2 phases with 8 dogs per group. In the first phase the dogs were administered 0, 20 or 30 mg/kg orally once daily for 7 days and in the second phase 0, 40, or 50 mg/kg once daily for 7 days. CERENIA Tablets administered at 20 and 30 mg/kg caused occasional vomiting. CERENIA Tablets administered at 40 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg caused clinically relevant signs of weight loss, vomiting, soft stools, weakness, lethargy, salivation and hypokalemia. Additionally, leukopenia characterized by a neutropenia and a trend toward decreasing plasma phosphorus values was seen. Decreased heart rate and prolonged corrected QT intervals were seen in all treatment groups in a dose dependent manner.
Twenty-four Beagle dogs (12 males and 12 females) approximately 28 weeks of age were administered maropitant (mesylate salt) orally once daily for 90 days at 0, 1, 5, and 20 mg/kg. End of study body weights in the 20 mg/kg group were 8-15% lower than baseline body weights.
STORAGE CONDITIONS
CERENIA Tablets should be stored at controlled room temperature 20°–25°C (68°–77°F) with excursions between 15°–30°C (59°–86°F).
HOW SUPPLIED
CERENIA peach-colored tablets are scored with a break line, and contain 16, 24, 60 or 160 mg of maropitant as maropitant citrate per tablet. Each tablet is marked with "MPT" and the tablet strength. Each tablet size is packaged in a bottle containing 60 tablets and packaged in blister packs containing 4 tablets per perforated sheet.
NADA #141-262, Approved by FDA
Kalamazoo MI 49007
Revised: March 2016
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 16 mg Tablet Bottle Label
For oral use in dogs only
NET CONTENTS: 60 tablets
NADA # 141-262, Approved by FDA
Kalamazoo, MI 49007

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 24 mg Tablet Bottle Label
For oral use in dogs only
NET CONTENTS: 60 tablets
Approved by FDA
Kalamazoo, MI 49007

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 60 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NET CONTENTS: 60 tablets
Approved by FDA
Kalamazoo, MI 49007

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 160 mg Tablet Bottle Label
For oral use in dogs only
NET CONTENTS: 60 tablets
Approved by FDA
Kalamazoo, MI 49007

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 16 mg Tablet Foil
(maropitant citrate) 7oetis
See package insert for complete product information. 16 mg

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 24 mg Tablet foil
(maropitant citrate) 7oetis
See package insert for complete product information. 24mg

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 60 mg Tablet foil
(maropitant citrate) 7oetis
See package insert for complete product information. 60 mg

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 160 mg Tablet Foil
(maropitant citrate) 7oetis
See package insert for complete product information. 160 mg
Cerenia hund
Already have a VetUK Account?
Don't have an account?
Cerenia Tablets for dogs contain 16 mg, 24 mg, 60 mg or 160 mg maropitant as maropitant citrate monohydrate. The tablets also contain Sunset Yellow (E110) as a colourant. The tablets are pale orange and have a score line on both sides allowing the tablet to be halved. Each tablet is marked with the Pfizer logo on the reverse side. On the obverse side, each half is marked with the letters "MPT" and figures denoting the quantity of maropitant.

Cerenia 160mg Tablet
Cerenia tablets contain boxmaropitant citrate monohydrate. Indicated for the prevention of vomiting including that induced by chemotherapy, in conjunction with cerenia solution for. [More info]

Cerenia 16mg Tablet
Cerenia tablets contain boxmaropitant citrate monohydrate. Indicated for the prevention of vomiting including that induced by chemotherapy, in conjunction with cerenia solution for. [More info]

Cerenia 24mg Tablet
Cerenia tablets contain boxmaropitant citrate monohydrate. Indicated for the prevention of vomiting including that induced by chemotherapy, in conjunction with cerenia solution for. [More info]

Cerenia 60mg Tablet
Cerenia tablets contain boxmaropitant citrate monohydrate. Indicated for the prevention of vomiting including that induced by chemotherapy, in conjunction with cerenia solution for. [More info]
Cerenia tablets are indicated for the prevention of nausea induced by chemotherapy. For the treatment of vomiting, in conjunction with Cerenia Solution for Injection and in combination with other supportive measures. For the prevention of vomiting including that induced by motion sickness.Also the prevention of nausea induced by chemotherapy and treatment and prevention of vomiting (except motion sickness)
Cerenia tablets should be administered once daily, at a dose of 2 mg maropitant per kg bodyweight, using the number of tablets given in the table below. Tablets are breakable along the score line on the tablet.
To prevent vomiting, tablets should be given more than 1 hour in advance. The duration of the effect is approximately 24 hours and, therefore, tablets can be given the night before administration of an agent that may cause emesis (e.g. chemotherapy).
Cerenia can be used as either tablets or Solution for Injection once daily for up to five consecutive days to treat vomiting.
Cerenia tablets are effective in the treatment of vomiting, however in cases of frequent vomiting it is recommended to initiate treatment with Cerenia Solution for Injection.
Treatment and prevention of vomiting (except motion sickness)
Cerenia tablets should be administered once daily, at a dose of 8 mg maropitant per kg bodyweight, using the numbers of tablets given in the table below. Tablets are breakable along the score line on the tablet.
Tablets should be administered at least one hour before starting the journey. The anti-emetic effect persists for at least 12 hours, which for convenience may allow administration the night before early morning travel. Treatment may be repeated for a maximum of two consecutive days.
In some individual dogs and when repeating the treatment, lower doses than recommended might be sufficient.
Prevention of motion sickness only
Firstly, fold or cut along the perforation between each tablet as shown by the scissor symbol. Find the pull-back notch (or cut) as shown by the arrow symbol. Holding one side of the cut firmly, pull the other side towards the centre of the blister until the tablet is visible. Remove table from blister and administer as instructed.
Note: No attempt should be made to remove the tablet by pushing it through the blister backing as this will damage both the tablet and blister.
A light meal or snack before dosing is recommended; prolonged fasting before administration should be avoided. Cerenia tablets should not be administered wrapped or encapsulated in food as this may delay dissolution of the tablet and consequently the onset of the effect.
Dogs should be carefully observed following administration to ensure that each tablet is swallowed.
Vomiting can be associated with serious, severely debilitating conditions including gastrointestinal obstructions; therefore, appropriate diagnostic evaluations should be employed.
Administering Cerenia on a completely empty stomach may cause the dog to vomit. A light snack before dosing could help prevent this effect.
The safety of Cerenia has not been established in dogs less than 16 weeks of age and in pregnant or lactating bitches. Use only according to a risk benefit assessment by the responsible veterinary surgeon.
Cerenia should be used in conjunction with other supportive measures if appropriate.
Clinical signs including vomiting on first administration, excess salivation and watery faeces have been observed when the product has been overdosed in excess of 20 mg/kg.
Maropitant is metabolised in the liver and therefore should be used with caution in dogs with liver disease.
Cerenia should be used with caution in animals suffering from or with a predisposition for heart diseases. Cerenia should not be used concomitantly with Ca-channel antagonists as maropitant has affinity to Ca-channels.
Maropitant is highly bound to plasma proteins and may compete with other highly bound drugs.
Cerenia is not a sedative and some motion sick dogs may show nausea-like signs during travel such as salivation and lethargy. These signs are temporary and should resolve when the journey ends.
Incidents of pre-travel vomiting, usually within two hours post-dosing, were commonly reported after administration of the 8 mg/kg dose.
Wash hands after use. In case of accidental ingestion seek medical advice immediately and show the package leaflet or the label to the physician.
This veterinary medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions.
Half tablets should be stored for a maximum of two days after removal from the blister. Half-tablets should be returned to the opened blister and kept within the cardboard outer.
Any unused veterinary medicinal product or waste materials derived from such veterinary medicinal products should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children. For animal treatment only.
Cerenia tablets are supplied in blister packs with four tablets per pack.
Cerenia hund
TANYAS UMFASSENDES HANDBUCH
ЬBER CHRONISCHE NIERENERKRANKUNG (CNE)
ЬBELKEIT, ERBRECHEN, APPETITVERLUST UND
Ьbelkeit, Erbrechen und Appetitverlust gehцren mit zu den am hдufigsten auftretenden Gesundheitsproblemen von CNI-Katzen.
Es gibt eine ganze Reihe unterschiedlicher Grьnde, die dafьr verantwortlich sein kцnnen. Bei einer CNI- Katze kann aber auch mehr als nur ein Problem fьr das Auftreten dieser Symptome verantwortlich sein.
Glьcklicherweise gibt es in den meisten Fдllen Mittel, die ihr helfen, dass sie sich wieder besser fьhlt. Aber um das richtige Medikament einsetzen zu kцnnen, mьssen Sie den Grund kennen.
Ein Ьberschuss an Magensдure ist der wahrscheinlichste Ьbeltдter bei Katzen, deren Kreatininwert ьber 3 mg/dl oder 265 µmol/L (international) liegt, obwohl das auch bei Katzen mit einem niedrigeren Kreatininwert auftritt. Gegen eine ьberschieЯende Magensдure gibt es ein i ge Behandlungsmцglichkeiten, die helfen kцnnen .
Halten die Magenprobleme Ihrer Katze trotz der Behandlung des Magensдureьberschusses und anderer mцglicher Ursachen an, dann gibt es noch weitere Behandlung en , die Sie dabei unterstьtz en , die Ьbelkeit und das Erbrechen unter Kontrolle zu bringen.
Beachten Sie bitte, dass ein Magensдureьberschuss nicht dasselbe ist wie eine Metabolische Azidose .
Ursachen fьr Ьbelkeit, Erbrechen und Appetitverlust
Leider gibt es eine groЯe Anzahl mцglicher Auslцser fьr Ьbelkeit, Erbrechen und Appetitverlust bei CNI-Katzen. Daher kann es verwirrend sein, herauszufinden, was der Auslцser im Fall Ihrer Katze sein kцnnte. Um es einzugrenzen, empfehle ich Ihnen die Liste der Symptome auf der Seite Verzeichnis der Symptome und Behandlungsmцglichkeiten durchzugehen und zu ьberlegen, welche davon Ihnen bekannt vorkommen.
Alternativ dazu beschreibt die Aufzдhlung unten e in ig e der mцg liche n Auslцser von Ьbelkeit, Erbrechen und Appetitverlust. Ist Ihnen jedoch ein Problem Ihrer Katze bereits bekannt, beispielsweise ein zu hoher Phosphatspiegel, dann klicken Sie auf den entsprechenden Link. Er fьhrt Sie zu Informationen ьber weitere Symptome, die mit diesem Befinden zusammenhдngen. Das hilft Ihnen bei der Eingrenzung des Problems.
Antibiotika kцnnen bei manchen Katzen Ьbelkeit und Erbrechen verursachen.
Verstopfung kann beim Toilettengang Erbrechen verursachen.
Bitten Sie Ihren TA darum, einige dieser Ursachen auszuschlieЯen oder - wenn vorhanden - zu behandeln. Die Behandlung der Symptome hilft nicht nur das Erbrechen oder den Appetitverlust zu beseitigen und damit das Wohlbefinden Ihrer Katze zu fцrdern, manchmal hilft es auch (z.B. durch die Kontrolle erhцhter Phosphatspiegel), das Voranschreiten der CNI zu verlangsamen.
Why so many vomiting cats? Getting the diagnosis (2011) ist ein Vortrag von Dr. S. Little auf dem 36. World Small Animal Veterinary Association World Congress, bei dem ein Ablaufdiagramm gezeigt wird, um die Grьnde eines Erbrechens einzugrenzen.
Gifte, inkl usiv Magensдure ьberschuss
W enn Sie die oben genannten Grьnde ausschlieЯen kцnnen oder behandelt haben, mag es sein, dass Ihre Katze sich immer noch erbricht , ihr weiterhin ьbel ist , und sie nicht fressen will. In solchen Fдllen kцnnte das Problem durch Gifte verursacht werden , insbesondere durch einen Magensдureьberschuss. An irgendeinem Punkt der Krankheit wird so gut wie jede CNI- Katze Probleme mit der Magensдure haben. Daher ist die Wahrscheinlichkeit hoch, dass Sie diese Seite lesen mьssen, aber auch dann, wenn Ihre Katze noch einige andere der o.g. Probleme hat. Sehen Sie sich unten die Symptomliste an, und ьberprьfen Sie, ob Ihnen etwas davon bekannt vorkommt - bei den meisten Menschen ist das der Fall.
Gastrin ist ein gastro-intestinales Hormon, das die Sekretion von Magensдure anregt, die den Magen bei der Verdauung unterstьtzt. Die Nieren sind verantwortlich fьr die Ausscheidung von Gastrin, aber bei CNI kцnnen sie dieser Aufgabe nicht mehr so gut nachkommen. Als Folge davon bleibt Gastrin im Magen und regt die Produktion ьberschьssiger Magensдure an. Dieses ЬbermaЯ an Magensдure fьhrt dazu, dass die Katze sich sehr schlecht fьhlt. In schweren Fдllen entstehen Geschwьre, die eine g astrointestinale Blutung auslцsen kцnnen.
Im Allgemeinen muss man davon ausgehen, dass Katzen mit einem Kreatininwert ьber 3 mg/dl oder 265 µmol/L Unterstьtzung bei der Kontrolle der ьberschьssigen Magensдure benцtigen. Je hцher BUN oder Harnstoff bei Ihrer Katze liegen, um so ьbler fьhlt sie sich und erbricht.
Magensдureьberschuss kann dazu fьhren, dass manche Katzen sich sehr krank fьhlen, aber das ist auch immer von der Katze abhдngig. Mein Thomas erbrach sich nie, selbst dann nicht, als sein Kreatininspiegel ьber 7 lag und sein BUN ьber 100 war. Aber einige Katzen erbrechen schon, wenn ihre Blutwerte nur leicht ьber der Referenz liegen.
Auch wenn Harnstickstoff selbst kein Gift ist, gibt es doch einen Zusammenhang mit anderen Toxinen, die weniger leicht zu messen sind. Daher: Je hцher BUN oder Harnstoffspiegel ist, umso hцher liegt der allgemeine Giftspiegel, und damit steigt wiederum die Wahrscheinlichkeit, dass die Katze sich krank fьhlt und erbricht.
Liegen die Blutwerte Ihrer Katze noch ziemlich niedrig (Kreatinin in den 2 bis in die niedrigen 3 mg/dl oder 200 bis 300 µmol/L ) , aber trotzdem erbricht sie sich hдufig, dann bitten Sie Ihren TA darum, eine Pankreatitis auszuschlieЯen.
Es gibt keinen Test fьr einen Magensдureьberschuss, aber hier sind einige von den Symptomen, die Sie wahrscheinlich beobachten werden (sie kцnnen auch auf andere Ursachen zurьckzufьhren sein, wie in jeder Kategorie ausgefьhrt):
Appetitverlust ist sehr hдufig bei CNI-Katzen und oft durch einen Magensдureьberschuss verursacht. Menschliche CNI-Patienten berichten ьber einen beeintrдchtigten Geruchs- und manchmal auch Geschmackssinn. Man vermutet, dass die urдmischen Gifte dafьr verantwortlich sind. Es ist anzunehmen, dass das auch bei Katzen der Fall ist.
Katzen, die nicht fressen, laufen Gefahr, eine lebensbedrohliche Krankheit zu bekommen, genannt „hepatische Lipidose": Bei Mar Vista Vet finden Sie mehr Informationen darьber. Die Praxis Tierдrztliche Spezialisten bietet eine kurze Information fьr Katzenhalter. Aus diesem Grund ist es wichtig, dass Sie die Ursache fьr den Appetitverlust herausfinden und so schnell wie mцglich behandeln.
Eine Ьbelkeit ist nicht leicht festzustellen, meistens zeigt sie sich durch Appetitmangel. Mцglich ist auch, dass die Katze sich zusammenkauert und sichtbar unwohl fьhlt.
Ein hoher Phosphatspiegel , Austrocknung oder eine Anдmie kцnnen ebenfalls Ьbelkeit auslцsen.
CNI-Katzen erbrechen hдufig. Es kann als Einzelsymptom auftreten oder in Verbindung mit anderen Symptomen aus diesem Kapitel. Viele Katzen mit Magensдure ьberschuss oder Urдmie erbrechen sich ohne Behandlung regelmдЯig.
Manchmal findet sich im Erbrochenen Blut. Hellrotes Blut ist frisch, wдhrend дlteres Blut wie Kaffeesatz aussieht. Das kann ein Hinweis auf Mundgeschwьre oder auf gastrointestinale Blutungen sein. Wenn Sie das beobachten, sollten Sie sofort einen TA aufsuchen. Unser George, keine CNI-Katze, erbrach altes Blut als erstes Anzeichen seiner schweren Lebererkrankung.
Katzen, die sich hдufig ьbergeben, sind auch einem hцheren Austrocknungsrisiko ausgesetzt.
Es gibt einen Unterschied zwischen Erbrechen und Regurgitieren. Erbrechen wird normalerweise von heftigen Bauchbewegungen begleitet. Regurgitieren tritt plцtzlich auf und mit weniger Vorwarnung, wenn das Futter noch nicht im Magen war. Erbrechen bedeutet, dass der Mageninhalt herauskommt, beim Regurgitieren hat das Futter den Magen noch nicht erreicht, sondern es wird mehr oder weniger unverdaut aus der Speiserцhre gestoЯen. Die Ursache fьr Regurgitieren ist hдufig zu hastiges Fressen oder verschluckte Haarbдlle. Regurgitiertes sieht hдufig aus wie eine Wurst. The American Association of Feline Practitioners erklдrt den Unterschied und verlinkt zu einer Reihe von Webseiten. Auf einer wird eine Katze gezeigt, die sich erbricht. Die Tierklinik am Kaiserberg erklдrt den Unterschied auf Deutsch.
Bei Katzen, die sofort nach dem Fressen erbrechen, kann auch ein Problem bei der Magenentleerung vorliegen. Ranitidin kann dabei helfen.
Auch eine Verstopfung kann manchmal Erbrechen auslцsen, insbesondere dann, wenn Ihre Katze vor, wдhrend oder sofort nach der Benutzung des Katzenklos erbricht.
Wenn Sie Ihrer Katze subkutane Infusionen verabreichen, und sie regelmдЯig danach erbricht, liegt die Ursache mцglicherweise bei der verabreichten Infusionslцsung.
Gastrointestinalerkrankungen bei Hund und Katze ist ein Vortrag von Dr. Birgit Drescher. Scrollen Sie runter bis Punkt 2.
TA-Praxis van Loosen informiert zum Thema „Erbrechen von Katzen".
Coco's page - hier finden Sie praktische Ratschlдge von einem betroffenen Katzenhalter
Vet Info hat ebenfalls Informationen zum Thema Erbrechen.
Managing vomiting in cats: what's new for an old problem (2008) Zoran DL Presentation to the 2008 Nestlй Purina Veterinary Symposium zeigt einen Ьberblick ьber Erbrechen bei Katzen.
Erbrechen von klarem oder weiЯem Schaum
Im Erbrochenen findet sich nicht nur Futter. Das klassische Symptom bei Magensдureьberschuss ist das Erbrechen von klarem oder weiЯem Schaum. Dies ist hдufig das erste Anzeichen, das Menschen bemerken, wenn Ihre Katze eine CNI entwickelt.
Erbrechen von Wasser
Manchmal trinken CNI-Katzen auf einmal sehr viel Wasser und erbrechen anschlieЯend das meiste davon gleich wieder. Auch das kann ein Hinweis auf einen Magensдureьberschuss sein. Es ist mцglich, dass die Katze das Bedьrfnis hat viel zu trinken, um so die Magensдure zu verdьnnen.
Das kann ein Anzeichen fьr Ьbelkeit und Magensдureьberschuss sein. Aber auch fьr Austrocknung . Weniger hдufig tritt es bei einer Anдmie auf. In seltenen Fдllen ist es eine Nebenwirkung von Metoclopramid (MCP-Tropfen), wenn sie ьber einen lдngeren Zeitraum (mehr als drei Monate) verabreicht wurden.
Katzen mit zuviel Magensдure kцnnen mit den Zдhnen knirschen. Zahnerkrankungen sind eine weitere Ursache. Es kann auch auf eine Austrocknung hinweisen. Sehr selten ist es ein Hinweis auf einen „Gummikiefer", der durch die Krankheit Sekundдrer Hyperparathyreoidismus verursacht wird, eine Folge von CNI.
Animal Dental Center of Milwaukee and Oshkosh erklдrt die verschiedenen Ursachen von Zдhneknirschen bei Katzen.
Youtube zeigt das Video einer zдhneknirschenden Katze.
CNI-Katzen werden manchmal heiser durch den Rьckfluss der Magensдureьberschuss in die Speiserцhre.
In einigen Fдllen wird das aber auch durch einen niedrigen Kaliumspiegel ausgelцst. Heiserkeit tritt auch manchmal bei Katzen mit einer Schilddrьsenьberfunktion auf. Wenn zusдtzlich noch Husten auftritt, dann wдre eine mцgliche Ursache eine Flьssigkeitsansammlung und/oder Herzerkrankungen.
Sabbern kann bei Katzen durch einen Magensдureьberschuss ausgelцst werden. Zahnerkrankungen oder Mundgeschwьre sind weitere Mцglichkeiten. Manhattan Cat Specialists bieten mehr Informationen ьber Sabbern an. Dr. Elaine Wexler-Mitchell bietet auf Deutsch einen informativen Ьberblick ьber Zunge und Geschmackssinn der Katze an, in dem auch die mцglichen Ursachen fьr ьbermдЯigen Speichelfluss erklдrt werden.
Katzen fressen gerne Gras, damit sie erbrechen kцnnen. Hдufiger Grund dafьr ist, damit sie verschluckte Haarbдlle ausspucken kцnnen. Manchmal ist das auch bei CNI-Katzen die Ursache. Wenn einer CNI-Katze jedoch ohnehin schon aufgrund der Krankheit ьbel ist und nicht wegen der verschluckten Haare, dann fьhlt sie sich durch das Erbrechen etwas besser und frisst daher Gras, um erbrechen zu kцnnen. Normalerweise ist es vцllig in Ordnung, wenn Sie Ihre CNI-Katze Gras fressen lassen, solange es nicht mit Pestiziden behandelt wurde.
Gдhnen und Heulen
Das sind manchmal Symptome einer Magenьbersдuerung. Heulen kann auch andere Ursachen haben (siehe Verzeichnis der Symptome und Behandlungsmцglichkeiten ).
Kauern ьber der Wasserschьssel
Das kann ein Zeichen von Ьbelkeit und Magensдureьberschuss sein. Manchmal ist es auch ein Hinweis auf Austrocknung .
Spielen mit Wasser
Einige Katzen spielen schon von Anfang an gerne mit Wasser. Aber bei manchen CNI-Katzen entwickelt es sich zu einer Obsession, und sie spielen mit ihrer Wasserschьssel oder patschen ins Wasser. Vielleicht fallen Ihnen auch andere neue Eigenarten auf wie Trinken aus der Dusche oder dem Abfluss. Oder sie stehen auf dem Waschbecken und betteln nach frisch laufendem Wasser aus dem Hahn. Alle diese Verhaltensformen kцnnen auf einen Magensдureьberschuss hinweisen. Andere mцgliche Ursachen sind Austrocknung oder Diabetes .
Schnьffeln oder Lecken am Futter, dann Weggehen
Die Katze geht zur Futterschьssel und schnьffelt oder leckt am Futter, geht dann wieder weg. Das ist ein klassisches Anzeichen eines Magensдureьberschusses. Aber es kann auch ein Hinweis auf Mundgeschwьre sein.
Mit der Pfote ans Maul tatzen
Die hдufigste Ursache dafьr sind Zahnerkrankungen , aber manchmal ist es auch ein Zeichen von einem Magensдure ьberschuss .
Vermehrtes Trinken tritt recht hдufig auf bei CNI-Katzen. Normalerweise fдllt es ihnen schwer, eine Austrocknung zu vermeiden. Es kann aber auch ein Hinweis auf einen Magensдureьberschuss sein. In einigen Fдllen ist es auch ein Hinweis auf Diabetes .
Nur die SoЯe abschlecken
Die Katze leckt nur die SoЯe ab und lдsst die festen Futterbestandteile liegen. Das muss nicht bei allen Katzen ein Hinweis auf einen Magensдureьberschuss bedeuten, nur wenn es eine neue Angewohnheit ist – meine Katzen machen das immer, und sie sind alle gesund. Sie ziehen einfach nur die Patй-Futtersorten vor.
Manchmal kann es auch ein Hinweis auf eine Zahnerkrankungen sein.
Manche Katzen mit zuviel Magensдure haben Bauchschmerzen. Sie sitzen dann zusammengekauert in einer unbequemen Stellung. Im schlimmsten Fall kann dies ein Hinweis auf einen Zusammenbruch sein.
Die richtige Behandlung von Erbrechen, Ьbelkeit und Appetitverlust hдngt von der Ursache des Problems ab. Auf der Seite Verzeichnis der Symptome und Behandlungsmцglichkeiten finden Sie Informationen zu den BehandlungsmaЯnahmen zu den jeweils oben genannten Ursachen.
Es gibt keinen speziellen Test, um Gifte, besonders einen Magensдureьberschuss, zu diagnostizieren. Aber wenn Ihre Katze Anzeichen dafьr zeigt (z. B. Erbrechen weiЯen Schaums), lohnt sich eine Behandlung, um zu sehen, ob die Katze sich anschlieЯend besser fьhlt. Hier finden Sie einen machbaren abgestuften Behandlungsplan, den Sie mit Ihrem TA besprechen kцnnen:
Fangen Sie mit diesen einfachen, natьrlichen BehandlungsmaЯnahmen an – bei manchen Katzen reicht das schon aus:
Wenn diese MaЯnahmen nach ungefдhr zwei Tagen keine Wirkung zeigen, machen Sie weiter mit den Histamin H2 Antagonisten . Das ist eine Medikamentengruppe, die hдufig zur Magensдure ьberschuss kontrolle eingesetzt wird. Diese helfen den meisten Katzen. Sie kцnnen sie auch zusammen mit den natьrlichen Mitteln einsetzen:
Wenn Ihre Katze immer noch mit den Symptomen kдmpft, ziehen Sie die nдchste Stufe, die Anti-nausea Medikamente mit hinzu. Diese Medikamente wirken normalerweise sehr effektiv bei Ьbelkeit und Erbrechen, und sind daher die beste Wahl fьr Katzen, die noch weitere Probleme haben wie z.B. mit der Magenmotorik oder auch bei Katzen mit zusдtzlichen Erkrankungen wie Pankreatitis oder IBD. Sie kцnnen normalerweise parallel zu den anderen oben beschriebenen Medikamenten genommen werden :
Fьr gewцhnlich ist es kein Risiko, mehr als eine dieser BehandlungsmaЯnahmen gleichzeitig einzusetzen, z.B. Slippery Elm Bark und Famotidin, aber besprechen Sie das zuerst mit Ihrem TA. Verwenden Sie nicht Pepto-Bismol oder Antazida wie Tums oder Mylanta .
How I treat uremic crises in dogs and cats with chronic kidney disease (2009) ist ein Vortrag von Dr. D. Polzin auf dem 34. World Small Animal Veterinary Association World Congress in dem er die verschiedenen Behandlungsmethoden erklдrt.
Das Gute bei diesen MaЯnahmen ist, dass sie nur wenig Mьhe machen, keinen groЯen Eingriff darstellen und mit wenig Aufwand verbunden sind, dafьr jedoch bei manchen Katzen дuЯerst wirksam sind. Ich empfehle daher, sie zuerst auszuprobieren, um zu sehen, ob sie ausreichend helfen. Wenn sie wirken, dann kцnnen Sie den Unterschied (z.B. weniger Erbrechen) innerhalb von wenigen Tagen erkennen.
Erhцhen der Futterschьsseln
Normalerweise ist beim Fressen das Maul einer Katze niedriger als ihr Magen. Aber bei CNI-Katzen kann das dazu fьhren, dass die Magensдure in die Speiserцhre lдuft und dadurch einen Magensдurereflux hervorruft. Durch eine Erhцhung der Futter- und Wasserschьsseln reduzieren Sie dieses Problem und ermutigen damit Ihre Katze, mehr zu essen und zu trinken.
Wenn Sie die Nдpfe auf einen umgedrehten Blumentopf stellen, ist das oft schon ausreichend als richtige Hцhe fьr Ihre Katze. Wдhlen Sie einen Blumentopf mit der ungefдhren GrцЯe Ihrer Katze. Manche Tierlдden verkaufen auch Nдpfe auf Beinen, die ungefдhr 15 cm hoch sind.
Classy Cat Dishes verkauft Steingutnдpfe fьr ungefдhr US$25. Ich habe einige davon, und meine Katzen lieben sie. Meine Katzen sind nicht an CNI erkrankt, aber ich habe festgestellt, dass sie mehr futtern, wenn ich sie aus diesen Schьsseln fьttere.
Drs Foster & Smith verkauft Futterschьsseln auf einem schmiedeeisernen Stдnder fьr US$19,99. Sie haben auch noch andere erhцhte Nдpfe im Angebot.
Fьttern vor dem Schlafengehen
Sie werden vielleicht bemerken, dass sich die Magenbeschwerden Ihrer Katze nachts verschlimmern und sie sich erbricht oder gleich als erstes am Morgen. Das passiert, wenn eine Katze ьber einen lдngeren Zeitraum nichts zu Fressen bekommt. Die ьberschьssige Magensдure hat dann mehr Zeit, die Magenwдnde anzugreifen.
Zusдtzlich zu den anderen hier erwдhnten BehandlungsmaЯnahmen versuchen Sie sicherzustellen, dass Ihre Katze vor dem Schlafengehen frisst, um das zu vermeiden. Wenn Sie dafьr sorgen, dass sich immer Futter im Magen befindet bedeutet das, dass die Magensдure das Futter angreift statt der Magenwдnde. Mцglicherweise sollten Sie einen Futterautomaten aufstellen, damit Ihre Katze die ganze Nacht ьber mit Futter versorgt ist. Hier f inden Sie Links wo Sie solche Automaten finden.
Slippery Elm Bark
Wenn Sie natьrliche Methoden bevorzugen, um die Magensдureьberschuss unter Kontrolle zu halten und die damit verbundenen Begleitumstдnde wie Erbrechen, Ьbelkeit und Appetitverlust, dann ist ein pflanzliches Heilmittel, genannt Slippery Elm Bark (SEB), oft sehr wirksam. Es beruhigt den Verdauungstrakt und kann sowohl bei einer Verstopfung als auch bei Durchfall helfen. Bei Ganzheitlicher Behandlungsansatz finden Sie ausfьhrliche Informationen zu SEB.
Einsatz von Magensдureblockern (Histamin-H2-Antagonisten)
Das ist eine Medikamentengruppe, die дuЯerst wirksam ist bei der Kontrolle eines Magensдureьberschusses und dadurch Erbrechen und Ьbelkeit reduziert und den Appetit anregt.
Die meisten dieser Medikamente werden als Sдurebinder angesehen, dabei sind sie in Wirklichkeit Histamin-H2-Antagonisten, die die Produktion von Magensдure blockieren statt sie nur zu neutralisieren. Da sie lange wirken, sind sie in der Regel eine gute Wahl bei der Behandlung von Magensдureproblemen. In Current concepts for the management of chronic renal failure in the dog and cat - early diagnosis and supportive care (2005), einem Vortrag auf dem 30. World Congress of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association, weist Dr. Sherry Sanderson darauf hin, dass es generell ratsam ist, ab einem Kreatininwert ьber 3 mg/dl oder 265 µmol/L solche BehandlungsmaЯnahmen einzusetzen.
Obwohl diese Medikamente rezeptfrei erhдltlich sind, verabreichen Sie sie bitte NICHT, ohne vorher mit Ihrem TA darьber zu sprechen. Ganz besonders dann, wenn Ihre Katze sich bereits in einem fortgeschrittenen Stadium von CNI befindet. Sie werden ьber die Nieren ausgeschieden und kцnnten daher nicht mehr angebracht sein. Avoiding Adverse Drug Reactions (2001) ist ein Vortrag von Lauren Trepanier auf dem World Small Animal Veterinary Association World Congress 2001, in dem darauf hingewiesen wird, dass es klug ist, die Dosis dieser Medikamente bei CNI-Katzen zu reduzieren (scrollen Sie runter bis zum Ende).
Sobald sie einmal damit angefangen haben, diese Medikamente zu geben, ist es fьr gewцhnlich besser, wenn Sie sie weiterhin regelmдЯig verabreichen. Auch dann, wenn es Ihrer Katze scheinbar besser geht, damit sich nicht wieder erneut einen Magensдure ьberschuss aufbauen kann.
Vetion hat vier Magensдurehemmer verglichen (Test bei Hund en ): Ranitidin, Famotidin, Pantoprazol und Omeprazol.
Famotidin (Pepcid Akut)
Famotidin ( Pepcid AC ) ist das am hдufigsten eingesetzte Medikament bei den durch feline CNI verursachten Magensдureproblemen in den USA, und es ist ein sehr wirksames Medikament fьr Magensдьreьberschuss. Als Nebenwirkung kann Famotidin den Parathormonspiegel bei CNI-Katzen absenken. Famotidine reduces serum parathyroid hormone levels in uremic patients (1991) Arik N., Arinsoy T., Sayнn M ., Taşdemir I ., Yasavul U ., Turgan C ., Caglar S ., Nephron 59(2) p333 erklдren mehr dazu. Aber ich wьrde Famotidin nicht einsetzen, nur um einen erhцhten PTH-Spiegel abzusenken.
Der Wirkstoff ist Famotidin USP. Pepcid AC (die gebrдuchliche Stдrke) enthдlt 10 mg. Famotidin wird unter verschiedenen Namen verkauft (z.B. Amfamox, Famox oder Pepcidine in Neuseeland und Australien). General Medical gibt einen Ьberblick ьber die verschiedenen Handelsnamen unter denen Famotidin in verschiedenen Lдndern verkauft wird. In Deutschland heiЯt es Pepcid akut und ist unter der PZN (Pharmazentralnummer) 1826831 rezeptfrei in Apotheken erhдltlich.
Wenn Sie das Markenprodukt kaufen mцchten – es gibt eine ganze Reihe anderer Pepcid-Produkte – so stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie das richtige kaufen. Sie brauchen Pepcid AC oder Pepcid Akut, aber nicht die Kautablette und nicht Pepcid Complete. Beide enthalten einige Inhaltsstoffe, die sie fьr CNI-Katzen ungeeignet machen. Es gibt auЯerdem noch eine neue Version genannt Pepcid Maximum Strength. Das ist der gleiche Wirkstoff wie Pepcid AC, aber es enthдlt doppelt soviel Famotidin. Achten Sie also darauf, dass sie die richtige Stдrke kaufen (10 mg Tabletten).
Es sieht leider so aus, dass Pepcid AC in GB nicht mehr verkauft wird und durch PepcidTwo ersetzt wurde. PepcidTwo enthдlt zusдtzlich zu Famotidin noch Magnesium und Kalzium und ist daher fьr CNI-Katzen nicht geeignet. Famotidin gibt es auch als Generika in Apotheken, aber nur in der 20 mg Stдrke, die schwierig zu teilen ist. AuЯerdem benцtigen Sie dafьr ein Rezept von Ihrem TA. Wenn Sie wirklich Famotidin geben mцchten, dann kцnnen Sie es manchmal ьbe r Amazon UK in der 10 mg Stдrke zu Preisen von Ј5 bis 6 5 finden (geben Sie als Suchword Pepcid AC oder Famotidin ein). AuЯerdem stellt The Specials Laboratory es in katzengerechter GrцЯe her – 90 x 2,5 mg Kapseln kosten Ј93,79 plus 20 Prozent Steuern, die Versandkosten liegen bei ungefдhr Ј12,50. Sie verkaufen auЯerdem 100 ml Famotidin. 2,5 mg pro ml fьr Ј91,89. Das Ablaufdatum liegt bei 90 Tagen nach Herstellung. Wenn Sie solche Preise nicht bezahlen mцchten, rate ich Ihnen stattdessen zu Ranitidin.
Netdoktor hat Informationen auf Deutsch ьber Famotidin.
Famotidin wird von den Nieren ausgeschieden, und Katzen mit CNI kцnnen es nicht so effektiv verstoffwechseln wie gesunde Katzen. Das bedeutet, es kann sich im Kцrper der Katze anreichern und dann Probleme verursachen. The US Food & Drug Administration bietet Information an, warum es ratsam ist, die normale Dosis bei (menschlichen) CNI Patienten zu reduzieren. Avoiding Adverse Drug Reactions (2001), ist ein Papier von Lauren Trepanier vom World Small Animal Veterinary Association World Congress 2001. Es besagt, dass es klug ist, sich bei CNI-Katzen ebenfalls daran zu halten (scrollen Sie zum Ende).
Hier sind Vorschlдge zur Dosierung von Pepcid AC, aber lassen Sie sich von Ihrem Tierarzt beraten. Sie sollten Pepcid AC nur mit der Zustimmung Ihres Tierarztes einsetzen. Beginnen Sie nicht mit der Hцchstdosis, das kцnnte riskant sein.
2.5 mg einmal jeden zweiten Tag (d.h. ein Viertel einer 10mg Tablette einmal jeden zweiten Tag, z.B. Mo, Mi, Fr )
Mittlere Dosis (falls die Anfangsdosis nicht zu helfen scheint):
2.5mg einmal tдglich ( d.h. ein Viertel einer 10mg Tablette einmal tдglich)
2.5mg zweimal tдglich ( d.h. ein Viertel einer 10mg Tablette zweimal tдglich , 5mg am Tag insgesamt)
Wenn Sie Famotidin nur einmal tдglich geben, dann empfehle ich dafьr die Schlafengehenszeit, da das offensichtlich hilfreich ist fьr Katzen, die nachts oder sofort am Morgen erbrechen mьssen. Pepcid schmeckt sehr bitter und kann dazu fьhren, dass die Katzen aus dem Maul schдumen. Es ist daher vermutlich einfacher, wenn Sie es bevor Sie es Ihrer Katze geben, in einer Gelkapsel verpacken. Pepcid wirkt normalerweise ziemlich schnell, meistens innerhalb von zwei Tagen.
Some people find that after a while, famotidine seems to be less effective. If you are using a low dose, increasing the dose as outlined above might help. Evaluating the prolonged use of an antacid, famotidine, in cats is a study funded by the Winn Feline Foundation in 2017 which will investigate if it does become ineffective in cats and whether changing the dose might help. Alternatively, you could ask your vet about switching to ranitidine.
Famotidin orale Suspension
Wenn Ihre Katze nicht leicht zu medikamentieren ist, kцnnen Sie Famotidin auch spritzen oder als orale Suspension verabreichen. Leider ist weder die orale noch die injizierbare Form in Deutschland erhдltlich.
Thriving Pets verkauft 10 mg/ml orale (flьssige) Suspension Version von Famotidin in einer 30 ml GrцЯe. Wenn Sie also die ьbliche Dosis von 2,5 mg geben mцchten, dann mьssen Sie 0,25 ml abmessen. Dieses Medikament hat eine kurze Verfallsdauer, Sie sollten daher nicht mehr bestellen als Sie ьber einen Zeitraum von 14 Tagen verbrauchen kцnnen (Lieferzeit mit eingerechnet). Genau wie die Tabletten ist auch diese Famotidinvariante sehr bitter. Wenn Sie Ihrer Katze keine bittere orale Medikamente verabreichen mцchten, dann sollten Sie stattdessen die injizierbare Form bevorzugen. Wenn Sie das Wort „Tanya“ (ohne die Anfьhrungsstriche) in den Gutscheincode schreiben, dann erhalten Sie zehn Prozent Nachlass auf jede Bestellung ьber 55 US$. Die Versandkosten sind ebenfalls frei, wenn der Bestellwert nach dem Gutscheincode noch ьber 55 US$ liegt , aber natьrlich nicht ins Ausland .
Famotidin zum Injizieren
Es gibt zwei Arten von injizierbarem Famotidin (leider ist keine in Deutschland erhдltlich). Einmal die 10 mg/ml Stдrke ohne Konservierungsstoffe. Sie ist in 2 ml-Ampullen erhдltlich. Da es keine Konservierungsstoffe enthдlt, ist die Haltbarkeit begrenzt (es ist als Einmalgabe bei Menschen vorgesehen). Es gibt auch eine 10 mg/ml Stдrke in einer 20 ml-Ampulle, die Konservierungsstoffe enthдlt und wiederbenutzt werden kann, sollte aber im Kьhlschrank aufbewahrt werden.
Sie kцnnen die injizierbare Darreichungsform entweder tatsдchlich direkt Ihrer Katze spritzen oder durch die subkutanen Infusionen verabreichen, indem Sie sie einfach in den Port Ihres Infusionsbestecks spritzen. Es ist kein Problem, es ungefдhr eine halbe Stunde vorher herauszuholen, bevor Sie es verabreichen, damit es sich ein wenig erwдrmen kann.
Thriving Pets verkauft die 10 mg/ml injizierbare Variante von Famotidin in einer 20 ml GrцЯe. Wenn Sie daher die ьbliche Famotidin-Dosierung von 2,5 mg verabreichen mцchten, dann geben Sie 0,25 ml. Wenn Sie das Wort „Tanya“ (ohne die Anfьhrungsstriche) in den Gutscheincode schreiben, dann erhalten Sie zehn Prozent Nachlass auf jede Bestellung ьber 55 US$. Die Versandkosten sind ebenfalls frei, wenn der Bestellwert nach dem Gutscheincode noch ьber 55 US$ liegt , aber natьrlich nicht ins Ausland .
Famotidin Neben- und Wechselwirkungen
Die hдufigsten Nebenwirkungen bei Menschen sind Verstopfung oder Durchfall.
Einige Katzen, insbesondere jene mit hohen Blutwerten (Kreatinin ьber 450 µmol/L oder 5 mg/dl), vertragen Famotidin nicht so gut. Mцglich ist, dass ihre Nieren es nicht mehr ausreichend ausscheiden kцnnen wie oben beschrieben. Es kann sogar vorkommen, dass diese Katzen vermehrt erbrechen, wenn sie das Medikament bekommen. Das passierte unserem Thomas, und spдter dann auch Ollie. Drugs erwдhnt, wie eine Ьberdosis Erbrechen auslцsen kann. Wenn sich das Erbrechen und der Appetitverlust Ihrer Katze nach zwei Tagen mit Famotidin nicht verbessert haben, dann bitten Sie Ihren TA, zu Ranitidin zu wechseln.
Famotidin kann bei Katzen mit Herzrhythmusstцrungen auch unerwьnschte Auswirkungen haben. In solchen Fдllen sprechen Sie mit Ihrem TA, ob Sie nicht lieber zu Ranitidin wechseln sollten.
Medicine Net erwдhnt, dass Famotidin bei Menschen eine Anдmie hervorrufen kann. Web MD berichtet von menschlichen CNI-Patienten, die durch Famotidin ungewцhnlich schlдfrig wurden.
Famotidine kann Wechselwirkungen mit Antibiotika aus der Familie der Cephalosporine wie Convenia eingehen. Deshalb sollten Sie sie mit zweistьndigem Abstand voneinander geben.
Famotidine may reduce the absorption of vitamin B12 from food, so it might be worth supplementing vitamin B12.
Ich empfahl frьher, Famotidin mit mindestens zweistьndigem Abstand zu Sucralfat (Carafate oder Antepsin) oder Metoclopramid (MCP-Tropfen) zu verabreichen. Der Grund war, dass laut Plumb's Veterinary Drug Handbook diese anderen Medikamente sich mit Famotidin verbinden kцnnten und deren Wirksamkeit dadurch herabgesetzt wird. In der neuesten Ausgabe von Plumb’s wird diese Anforderung jedoch nicht mehr erwдhnt. Es sieht demnach so aus, als mьsste man nun doch keinen zeitlichen Abstand mehr zu Famotidin einhalten. Onmeda warnt jedoch, dass Sucralfat die Aufnahme von Famotidin verringern kann.
RX Med behauptet, dass „der „gleichzeitige Einsatz von Aluminiumhydroxid/Magnesiumhydroxid in der ьblichen Dosierung keinen Einfluss hat auf die Pharmakodynamik und Bioverfьgbarkeit von Pepcid AC“ hat. Plumb’s empfiehlt jedoch immer noch, Famotidin zeitlich von der Verabreichung von Phosphatbindern und ACE-Hemmern zu trennen. Ich wьrde mich lieber auf die sichere Seite begeben und wenn mцglich, Famotidin weiterhin getrennt von Phosphatbindern und ACE-Hemmern verabreichen . Aber falls das, z.B. aufgrund Ihrer Arbeitszeiten, fьr Sie schwierig ist, geben Sie einfach Ihr Bestes.
Veterinary Partner bietet weitere Informationen zu Famotidin an und weist darauf hin, dass es bei Katzen mit Herzerkrankungen zu negativen Auswirkungen kommen kann.
Pet Place bietet weitere Informationen an ьber Famotidin (Sie mьssen sich nicht registrieren, klicken Sie bei dem Pop-up-Fenster unten einfach auf „close").
The Merck Manual bietet ebenfalls weiterfьhrende Informationen an ьber Famotidin und die mцglichen Nebenwirkungen bei Menschen.
Ein anderer beliebter frei verkдuflicher Histamin H2-Antagonist ist Ranitidin (Handelsname Zantic). Es wirkt дhnlich wie Famotidin. Einige Menschen ziehen Ranitidin vor, ganz besonders dann, wenn ihre Katze wegen Famotidin vermehrt erbrechen musste. Das kommt bei einer kleinen Anzahl von Katzen vor (fьr gewцhnlich dann, wenn der Kreatininwert ьber 450 µmol/L oder 5 mg/dl liegt).
Lt. Feline constipation, obstipation, and megacolon: prevention, diagnosis, and treatment Washabau R., einem Vortrag auf dem World Small Animal Veterinary Association World Congress 2001, hilft Ranitidin bei einigen Katzen auch bei Verstopfung.
Ranitidine tablets are widely available, either as a generic or under the trade name Zantac 75. In the USA they cost around US$20 for 80 75mg tablets. Zantac OTC has regular coupons available. In the UK they usually cost around Ј1.20 for 12 75 mg tablets tablets. Unfortunately in Australia it appears the smallest size available is now 150 mg, which is very difficult to divide into cat-sized doses.
The main problem with ranitidine tablets is dividing them up into cat-sized dosages - they usually have to be cut into eighths. If you find it hard to cut the pill into eight, you could try dissolving it in water and giving an eighth of the resulting mixture via syringe.
Ein Grund, warum sich einige Menschen gegen Ranitidin entscheiden ist, dass es normalerweise zweimal tдglich verabreicht werden muss, wohingegen Famotidin normalerweise nur jeden zweiten Tag gegeben werden muss, hin und wieder auch einmal tдglich.
Die ьbliche Dosis betrдgt 0,5 – 2,00 mg pro kg alle acht bis zwцlf Stunden. Die meisten Menschen finden, zweimal tдglich ist ausreichend.
Eine 4,5kg schwere Katze erhдlt also 2,5 - 10 mg zweimal tдglich.
Eine Standardtablette enthдlt 75mg. Eine 4,5 kg schwere Katze, die eine hцhere Dosis erhдlt, bekommt daher am einfachsten ein Achtel einer Tablette zweimal tдglich, (d.h 9,375 mg, oder etwas unter 10 mg).
Einige Menschen verabreichen bis zum Zweifachen dieser Menge. Aber genau wie bei Famotidin empfehle ich, niedrig zu beginnen und wenn nцtig die Dosierung anzuheben, da Ranitidin ebenfalls ьber die Nieren ausgeschieden wird. Lassen Sie sich von Ihrem TA beraten.
Ranitidin schmeckt bitter und kann dazu fьhren, dass die Katzen aus dem Maul schдumen. Es ist daher vielleicht besser, Sie verabreichen es in einer Gelkapsel. Viele Menschen ziehen es vor, die zweite tдgliche Dosis nachts vor dem Schlafengehen zu verabreichen, denn das hilft Katzen gegen nдchtliches oder morgendliches Erbrechen. Normalerweise wirkt es sehr schnell, innerhalb von zwei Tagen.
Das grцЯte Problem bei Ranitidin ist, die Tabletten in katzengerechte Dosen aufzuteilen. Wenn es Ihnen schwerfдllt, die Tablette in acht Teile zu schneiden, dann kцnnen Sie sie in Wasser auflцsen und ein Achtel der Mischung per Spritze verabreichen.
Ranitidin orale Suspension
Es gibt auch eine flьssige (sirupartige) Form von Zantic (nicht in Deutschland). Aber da sie nach Pfefferminze schmeckt, werden nicht viele Katzen sie mцgen. AuЯerdem ist sie verschreibungspflichtig. Bei Thriving Pets kцnnen Sie sie jedoch auch mit Rindfleischgeschmack anmischen lassen. Wenn Sie das Wort „Tanya“ (ohne die Anfьhrungsstriche) in den Gutscheincode schreiben, dann erhalten Sie zehn Prozent Nachlass auf jede Bestellung ьber 55 US$. Die Versandkosten sind ebenfalls frei, wenn der Bestellwert nach dem Gutscheincode noch ьber 55 US$ liegt , aber natьrlich nicht ins Ausland.
Es gibt auch eine injizierbare Form von Ranitidin, hergestellt von Bedford Laboratories . Sie ist verschreibungspflichtig und in den meisten amerikanischen Apotheken erhдltlich (mцglicherweise muss sie bestellt werden, in letzter Zeit scheint es immer hдufiger nicht auf Lager zu sein. Angeboten wird sie in einer 25 mg/ml Stдrke, gewцhnlich in einer 6 ml Ampulle.
E ine mцgliche Dosierung ist 0,3 ml zweimal tдglich, aber besprechen Sie das mit Ihrem TA. Sie kцnnen es entweder direkt Ihrer Katze spritzen, oder wenn sie Infusionen bekommt ьber die Infusionsflьssigkeit durch das Injektionszwischenstьck. Injizierbares Ranitidin muss im Kьhlschrank aufbewahrt werden. Es ist aber kein Problem, es ungefдhr eine halbe Stunde vorher herauszuholen bevor Sie es verabreichen, damit es sich ein wenig erwдrmen kann.
Thriving Pets verkauft injizierbares Ranitidin. Wenn Sie das Wort „Tanya“ (ohne die Anfьhrungsstriche) in den Gutscheincode schreiben, dann erhalten Sie zehn Prozent Nachlass auf jede Bestellung ьber 55 US$. Die Versandkosten sind ebenfalls frei (aber natьrlich nicht ins Ausland) , wenn der Bestellwert nach dem Gutscheincode noch ьber 55 US$ liegt.
Ranitidin Neben- und Wechselwirkungen
Ranitidin verursacht bei einig en Katzen Erbrechen und Durchfall. Genau wie Famotidin sollte es bei Katzen mit Herzgerдuschen nur sehr vorsichtig eingesetzt werden.
Plumb's Veterinary Drug Handbook empfiehlt, Ranitidin getrennt von Phosphatbindern zu verabreichen, aber Merck Veterinary Manual schreibt , dass Ranitidin gleichzeitig mit niedrig dosierten Phosphatbindern verabreicht werden kann . Sie empfehlen aber, Ranitidin mit einem Zeitabstand zu Sucralfat (Carafat, Antepsin bzw. Ulcogant) zu geben.
Ranitidine may reduce the absorption of vitamin B12 from food, so it might be worth supplementing vitamin B12.
Es ist auЯerdem ratsam, Ranitidin mit einem Zeitabstand zu ACE-Hemmern wie Fortekor zu geben. Aber wenn das fьr Sie aufgrund Ihrer Arbeitsverpflichtungen schwierig ist, dann geben Sie einfach Ihr Bestes.
Tierarzneimittelkompendium der Schweiz bietet auf Deutsch Informationen zu Ranitidin an.
Pet Place bietet Informationen zu Ranitidin an. (Sie mьssen sich nicht registrieren, klicken Sie bei dem Pop-up-Fenster unten einfach auf „close".)
Mцglicherweise bietet man Ihnen auch einen weiteren Wirkstoff aus dieser Familie an, genannt Cimetidin. Cimetidin hat viel mehr Wechselwirkungen mit anderen Medikamenten als Famotidin oder Ranitidin. Dazu gehцrt auch Amlodipin (ein Kalziumkanalblocker, der bei Herzerkrankungen eingesetzt wird oder zu hohem Blutdruck) und Diazepam (Valium), das manchmal als Appetitanreger verabreicht wird. Es hat auЯerdem einen ausgeprдgten Rebound-Effekt, d.h., nach Absetzen von Cimetidin tritt vorьbergehend ein Anstieg der Magensдure verstдrkt wieder auf. Aus diesem Grund schlage ich vor, Sie nehmen besser Famotidin oder Ranitidin.
Tierarzneimittelkompendium der Schweiz bietet Informationen auf Deutsch ьber Cimetidin an.
weist darauf hin, dass Cimetidin einen Anstieg des Kreatininspiegels verursachen kann. Wenn Sie Cimetidin verabreichen und der Kreatininspiegel steigt an, dann finden Sie heraus, ob sich das wieder bessert, wenn Sie das Medikament absetzen.
Top ten potential drug interactions on dogs and cats (2008) Trepanier LA Presentation to the World Small Animal Veterinary Association World Congress empfiehlt, besser Famotidin oder Ranitidin zu verabreichen statt Cimetidin.
Pet Place bietet Informationen an ьber Cimetidin (Sie mьssen sich nicht registrieren, klicken Sie bei dem Pop-up-Fenster unten einfach auf „close").
Andere BehandlungsmaЯnahmen: Medikamente gegen Ьbelkeit
Wenn die natьrlichen Behandlungsmethoden oben nicht ausreichen, und Ihre Katze nicht gut auf die Sдureblocker wie Famotidin anspricht (oder vielleicht zwar eine Verbesserung auftritt, sie aber immer noch ziemlich hдufig erbricht), dann ziehen Sie vielleicht eines dieser anderen Medikamente in Betracht. Diese Medikamente behandeln Ьbelkeit und/oder Erbrechen, aber sie funktionieren alle auf andere Art und Weise. Sprechen Sie mit Ihrem TA darьber, ob eines davon vielleicht passend fьr Ihre Katze sein kцnnte.
Treating feline pancreatitis (2009) Robertson J. DX Consult 2(1) bietet einen kurzen Ьberblick ьber diese drei Behandlungsmethoden.
Pharmacologic control of vomiting (2009) Tams T.R., erklдrt den Einsatz dieser und anderer Medikamente bei Katzen.
Omeprazol (Prilosec, Losec oder Omec)
Omeprazol gehцrt zur Medikamentengruppe der Protonenpumpenhemmer (PPH). Diese Medikamente sind keine Sдureblocker wie Famotidin (Pepcid) oder Ranitidin. Ihre Wirkungsweise beruht darauf, dass sie die vollstдndig blockieren , aber die PPH kцnnen das tun . Aus diesem Grund werden PPH hдufig zur Behandlung von Magengeschwьren eingesetzt.
Antisecretor activity of omeprazole in the conscious gastric fistula cat: comparison with famotidine (1989) Coruzzi G. & Bertaccini G., Pharmacological Research 21(5) pp499-506 f and heraus, dass Omeprazol „ungefдhr um das Fьnffache weniger wirkungsvoll als Famotidin ist“. Sie stellten fest, dass Omeprazol auf dem Hцhepunkt der Magensдureproduktion am wirksamsten ist. Sollte Ihre Katze jedoch aus irgendeinem Grund nicht gut auf Sдureblocker wie z.B. Famotidin ansprechen, dann kцnnen Sie Ihren TA bitten, ob Sie nicht Omeprazol ausprobieren kцnnen.
Zьricher Tierarzneimittelkompendium bietet Informationen ьber Omeprazol auf Deutsch an .
Die A potheken Umschau stellt den Beipackzettel ins Netz.
Pet Education bietet einige Informationen ьber Omeprazol an.
Veterinary Partner stellt ebenfalls einige Informationen zur Verfьgung.
Omeprazol ist sowohl als Tablette wie auch als Retardkapsel erhдltlich. Apparently the magnesium is there to help the capsule dissolve (it helps make it delayed release, so it reaches the stomach intact, where it is needed). Magnesium is not ideal for CKD cats, but at least some of the magnesium will be part of the capsule, which you discard.
Theoretisch sollte die Retardkapsel bei Katzen nicht eingesetzt werden, da Medikamente, die ihren Wirkstoff nur nach und nach freigeben, nicht geцffnet werden sollen. Aber eine ganze Kapsel ist zu viel fьr eine Katze. Einige Mitglieder von Tanya’s CKD Support Group und auch der Nierenkranke Katze Liste haben sie jedoch geцffnet und bei ihren Katzen erfolgreich eingesetzt. Besprechen Sie mit Ihrem TA, welche Darreichungsform Sie einsetzen sollten.
Wenn Ihr TA einverstanden ist, dass Sie die Kapseln nehmen, dann werden Sie feststellen, dass jede Kapsel kleine Kugeln (Mikrokugeln) enthдlt. Цffnen Sie eine Kapsel, und zдhlen Sie die darin enthaltenen Mikrokugeln. Die Anzahl differiert von Hersteller zu Hersteller. Sobald Sie wissen, wie viele Kьgelchen das von Ihnen eingesetzte Produkt enthдlt, kцnnen Sie die Dosis Ihrer Katze errechnen. Beispiel: Wenn eine 20 mg Kapsel 100 Kьgelchen enthдlt, und Sie mцchten Ihrer Katze 2,5 mg verabreichen, dann geben Sie ihr tдglich zwischen zwцlf und 13 Kugeln.
Omeprazol in der 20 mg Stдrke ist rezeptfrei in jeder Apotheke in D eutschland , Цsterreich und der Schwei z zu bekommen, der Preis fьr 14 Stьck liegt zwischen 6 und 10 Euro.
If the capsule you try has too many beads to count, try another brand. Walgreens and CVS both produce their own version of omeprazole capsules, but some members of my support group find the CVS brand has tiny beads which seem to carry a lot of static and are therefore very difficult to count. Altosec generic capsules apparently only contain about twenty beads.
Es ist nicht immer einfach, die Omeprazolkapseln in den USA zu finden. Hier sind zwei Bezugsadressen:
Walgreens verkauft 42 Kapseln in der 20,6 mg Stдrke fьr US$ 21.99
Amazon verkauft 42 Kapseln in der 20,6 mg Stдrke fьr US$ 23,88
Pet Place schreibt: „Die fьr Tiere gдngige Dosis ist alle 24 Stunden oder einmal tдglich 0,25 bis 0,5 mg pro Pfund Kцrpergewicht (0,5 bis 1,0 mg/kg).“ Eine 4,5 kg schwere Katze wьrde daher 2,5 bis 5 mg einmal tдglich bekommen.
The effect of orally administered ranitidine and once-daily or twice-daily orally administered omeprazole on intragastric pH in cats (2015) Љutalo S, Ruetten M, Hartnack S, Reusch CE & Kook PH Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 29(3) pp840-6 used a dosage of 1.1-1.3 mg/kg, in which case a 10 lb (4.5kg) cat would receive 5 to 5.85 mg.
That study assessed the effectiveness of once daily versus twice daily dosing and concluded that "twice-daily PO [orally] administered omeprazole significantly suppressed gastric acidity in healthy cats, whereas once-daily omeprazole and standard dosages of ranitidine were not effective acid suppressants in cats."
Some members of Tanya's CKD Support Group have therefore (with their vets' approval) started either increasing their cat's dose or dividing the total daily dose into two and giving it to their cats twice a day; in some cases they have done both. Many of those I hear from think this is helping their cats but, as ever, be guided by your vet regarding the best approach for your cat.
Omeprazol wird ьber die Leber und die Nieren ausgeschieden, daher ist es eventuell notwendig, die Dosis bei CNE-Katzen nach unten anzupassen. Besprechen Sie mit Ihrem TA, welches die richtige Dosis fьr Ihre Katze ist.
Anders als die Sдureblocker wie z.B. Famotidin (Pepcid) oder Ranitidin ist Omeprazol geschmacksneutral. Daher vermischen die meisten Menschen die errechnete Anzahl Mikrokugeln einfach mit dem Futter.
Einige Katzen reagieren innerhalb eines Tages auf Omeprazol, aber es kann auch bis zu einer Woche dauern, bis Sie eine Wirkung bemerken. Zur Ьberbrьckung dieses Zeitraums besprechen Sie mit Ihrem TA, ob Sie noch zusдtzlich Medikamente wie Famotidin geben sollen bis Omeprazol Wirkung zeigt.
Laut Plumb's Veterinary Handbook sind mцgliche Nebenwirkungen Ьbelkeit, Erbrechen und Durchfall. Auch Harnwegsinfektionen , eine Proteinurie oder Stцrungen des zentralen Nervensystems kцnnen auftreten. Bei Omeprazol kann es auch zu einer Abnahme der weiЯen Blutkцrperchen (Neutrophile) kommen, aber das ist selten.
Das V eterinдrkompendium der Schweiz listet die mцglichen Nebenwirkungen auf Deutsch auf.
Ein bekanntes Problem der Protonenpumpenhemmer ist, dass sie die Aufnahme von Nahrungsstoffen behindern kцnnen, insbesondere Vitamin B12 und Kalzium. Aus diesem Grund wird bei Menschen eine Verabreichungsdauer ьber einen Zeitraum von nur acht Wochen empfohlen. Adverse effects of long-term proton pump inhibitor therapy (2011) Sheen E. & Triadafilopoulos G., Digestive Diseases & Sciences 56(4) pp931-50 stellen fest, dass eine Langzeitbehandlung bei menschlichen Patienten zunimmt und untersuchten unter diesem Gesichtspunkt die mцglichen Nachteile. Die Studie fand heraus, dass bei den meisten Patienten die Vorteile einer langfristigen Behandlung die Risiken ьberwogen, aber dass дltere oder chronisch kranke Patienten „theoretisch bei einer Langzeitbehandlung ein hцheres Risiko eingehen.“
Plumb's Veterinary Handbook schreibt, dass man davon ausgeht, dass eine Behandlung von Hunden ьber einen Zeitraum von mindestens vier Wochen sicher ist. Es ist mir noch nicht gelungen, Aussagen ьber eine Behandlungsdauer bei Katzen zu finden. Aber ich kenne einige Menschen, die sie ihren Katzen stдndig geben. Wenn Sie sie ьber einen lдngeren Zeitraum verabreichen mцchten, dann besprechen Sie mit Ihrem TA, ob Sie zusдtzlich Vitamin B12 supplementieren oder die Dosierung erhцhen sollen.
Wenn die Omeprazolgabe eingestellt wird, kann es zu einem sog. „Rebound-Effekt“ kommen. D.h., es kann zu einem verstдrkten Ansteigen der Magensдureproduktion kommen, die sogar noch hцher liegt als vor der Behandlung. Bei Web MD finden Sie dazu Informationen. Die Д rzteZeitung дuЯert sich auf Deutsch zur Problematik.
Dieses Medikament wird normalerweise eingesetzt, um das Erbrechen von Katzen mit einer Pankreatitis oder Krebs zu kontrollieren. Ich habe zuerst im Jahr 2002 davon gehцrt, dass jemand Ondansetron bei einer CNI-Katze einsetzte. Aber bis vor kurzem war es kein gebrдuchliches Medikament bei Katzen, hauptsдchlich deshalb, weil es extrem teuer war. Seit vor kurzem eine generische Version in den USA erhдltlich ist, wird es langsam immer beliebter fьr CNI-Katzen. Nicht zuletzt deshalb weil es sehr wirksam ist.
Die Handelsnamen lauten u.a. Zofran in den USA, Setronon in Europa und Emeset in GB. Handelsnamen in Deutschland sind Axisetron oder Cellondan, Handelsnamen in Цsterreich sind Ondansan oder Zotrix. In Deutschland, Schweiz und Цsterreich gibt es Zofran und zahlreiche Generika. Es ist in Deutschland rezeptpflichtig.
Ondansetron wirkt auf eine andere Art und Weise als Metocolopramid unten (es ist ein selektiver Serotonin-5HT3-Rezeptor-Inhibitor), daher senkt es nicht den Anfallsschwellenwert ab, wie das bei Metocolopramid der Fall ist.
The Merck Veterinary Manual bietet kurze Informationen zu Ondansetron an.
Einige Menschen benutzen ein anderes Medikament aus dieser Familie, Dolasetron (Anzemet). Ich kenne nicht viele, die es bis heute bei ihrer CNI-Katze eingesetzt haben. Es scheint verbreiteter bei Katzen verwendet zu werden, die an einer Pankreatitis leiden. Pharmacologic control of vomiting (2009) Tams TR CVC in Kansas City Proceedings hat einige Informationen ьber Dolasetron. Ellviva bietet Informationen auf Deutsch an.
Ondansetron ist als 4 mg Tabletten erhдltlich. Die ьbliche Dosis betrдgt 1 mg tдglich. Eine Tablette besteht also aus vier Dosen. Das funktioniert gut bei vielen CNI-Katzen, aber Pet Place erwдhnt, dass die fьr Katzen ьbliche Dosis 0,11 mg pro Pfund Kцrpergewicht alle acht bis zwцlf Stunden betrдgt. Plumb's Veterinary Drug Handbook mentions an empiric dose of 0.5mg per kg bodyweight twice daily, so a 10 lb (4.5kg) cat would be given 2.25mg twice a day.
Oral, subcutaneous and intravenous pharmacokinetics of ondansetron in healthy cats (2014) Quimby JM, Lake RC, Hansen RJ, Lunghofer PJ & Gustafson DL Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 37(4) pp348–353 found that subcutaneous administration was more effective then oral dosing. It also states "twice daily administration at 0.5 mg/kg is likely inadequate to maintain serum concentrations within the therapeutic range; higher or more frequent doses may be needed." However, it further states that "the postulated therapeutic range - extrapolated from a previously published pharmacodynamic study - may not be accurate particularly if applied to repeated administration for chronic disease states." It further states that "A placebocontrolled clinical trial will be necessary to confirm which dose would be clinically effective for palliation of chronic nausea and vomiting in cats."
Obviously there are quite sizable differences between these doses. The above study found "Poor bioavailability should be taken into account when determining a route of administration for a patient as individual oral bioavailability ranged from 11 to 50% in the cats used in this study." For acute vomiting, such as in a cat with pancreatitis, higher and/or more frequent dosing may indeed be necessary. For chronic nausea in CKD cats, however, many people find the lower dose is fine, though they may need to give ondansetron twice daily. I would start with the lower dose of 1 mg each day, and if you find this is not enough, speak to your vet about increasing the dose or frequency.
Die Tabletten sind winzig, daher ist es schwer, sie in Viertel zu teilen.
Eine einzelne Tablette kann bis zu 6 US$ kosten. Sie sollten sich daher umsehen, denn es ist mцglich, das generische Produkt sehr viel gьnstiger zu bekommen. Costco apparently sell 60 4mg tablets for around US$23. In Deutschland bekommen Sie die Tabletten pro Stьck ab ca. Ђ7 gegen Rezept.
Health Warehouse verkauft 30 x 4 mg Tabletten Ondansetron fьr 22 US$ einschlieЯlich Versandkosten (in den USA) but the first order can take up to two weeks within the USA .
Thriving Pets verkauft Ondansetron fьr US$1 pro Tablette, oder 80 Cents pro Stьck, wenn Sie 30 kaufen. Es ist rezeptpflichtig. Wenn Sie das Wort „Tanya“ (ohne die Anfьhrungsstriche ) in den Gutscheincode schreiben, dann erhalten Sie zehn Prozent Nachlass auf jede Bestellung ьber 55 US$. Die Versandkosten sind ebenfalls frei, wenn der Bestellwert nach dem Gutscheincode noch ьber 55 US$ liegt , aber natьrlich nicht ins Ausland. .
Pharmplex Direct verkauft Ondansetron in GB fьr Ј7.49 fьr 30 plus Versandkosten (die Gesamtkosten liegen etwas unter Ј10). Es ist rezeptpflichtig.
Es gibt auch eine injizierbare Form von Ondansetron. Thriving Pets verkauft zehn Ampullen (4mg/2ml) fьr US$25. Wenn Sie das Wort „Tanya“ (ohne die Anfьhrungsstriche ) in den Gutscheincode schreiben, dann erhalten Sie zehn Prozent Nachlass auf jede Bestellung ьber 55 US$. Die Versandkosten sind ebenfalls frei, wenn der Bestellwert nach dem Gutscheincode noch ьber 55 US$ liegt , aber natьrlich nicht ins Ausland. .
Leider brennt die injizierbare Variante von Ondansetron sehr. Aber es kann eine gute Wahl sein bei einer Katze, die damit kдmpfen muss, ьberhaupt etwas bei sich zu behalten. Und es wirkt schnell. Die Wirkung sollte innerhalb von zwei Stunden eintreten.
Ondansetron Neben- und Wechselwirkungen
Mцgliche Nebenwirkungen sind Verstopfung, niedriger Blutdruck, oder Mьdigkeit. Menschen haben von schlimmen Kopfschmerzen berichtet. Drugs bietet weitere Informationen ьber Nebenwirkungen an.
Ondansetron kann aber auch Herzrhythmusstцrungen auslцsen. Im September 2011 warnte The US Food & Drug Administration , dass "Ondansetron das Risiko von ungewцhnlichen Verдnderungen in der elektrischen Aktivitдt des Herzens erhцhen kann, die wiederum zu mцglicherweise tцdlichen Herzarrhythmien fьhren kцnnen.“ Ellviva klдrt auf Deutsch ьber die Nebenwirkungen und Wechselwirkungen auf.
There is some debate as to whether ondansetron causes serotonin syndrome. The US Food & Drug Administration states that it may, though it says that "The majority of reports of serotonin syndrome related to 5-HT3 receptor antagonist use occurred in a post-anesthesia care unit or an infusion center." It also says that serotonin syndrome is more common when given at the same time as medications such as mirtazapine (used in CKD cats as an appetite stimulant). Drugs also mentions that using ondansetron and mirtazapine together may increase the risk. However, Can 5-HT3 antagonists really contribute to serotonin toxicity? A call for clarity and pharmacological law and order (2014) Rojas-Fernandez CH Drugs - Real World Outcomes 1(1) pp 3–5 disputes that ondansetron causes serotonin syndrome. Discuss with your vet whether to give both medications, and if you do so, give them at least two hours apart.
Ondansetron inhibits the analgesic effects of tramadol: a possible 5-HT3 spinal receptor involvement in acute pain in humans (2002) Arcioni R., della Rocca M., Romano S., Romano R., Pietropaoli P. & Gasparetto A., Anesthesia and Analgesia 94(6) pp1553-7 berichten, dass Ondansetron die schmerzstillende Wirkung von Tramadol bei bis zu 50 Prozent der menschlichen Patienten herabsetzt.
Maropitant (Cerenia) ist ein relativ neues Medikament von Pfizer. Die injizierbare Form ist in den USA zur Behandlung gegen Erbrechen und Ьbelkeit bei Katzen (und Hunden) zugelassen. In einigen Teilen Europas ist es auЯerdem noch gegen Reisekrankheit bei Katzen zugelassen. Treatment for visceral pain with the new NNK-1 receptor antagonist maropitant in cats (2011) Boscan P., Monnet E., Twedt D. & Nyiom S., fanden heraus, dass Maropitant auch ein wirksames Schmerzmittel sein kann.
Es muss nur einmal tдglich verabreicht werden und scheint bei einigen Katzen sehr wirksam zu sein. Die Wirkung tritt fьr gewцhnlich innerhalb einer Stunde ein. Es blockiert die Stimulation des Hirnbereichs, der Erbrechen auslцst. Ich mache mir Sorgen, dass das vielleicht bedeutet, dass der Katze immer noch ьbel sei, und sie daher nicht fressen mag, aber nicht mehr erbrechen kann. Wie auch immer, einige Menschen finden, dass Maropitant bei ihren Katzen besser wirkt als Ondansetron. Falls Sie daher mit der Wirkung von Ondansetron nicht zufrieden sind, kцnnen Sie es statt dessen mit Maropitant versuchen.
Maropitant ist als Injektion oder in Tablettenform erhдltlich. Sowohl die Injektion als auch die Tabletten sollen Erbrechen verhindern. Aber die injizierbare Variante ist auch als Mittel bei akutem Erbrechen konzipiert. Die Injektion scheint bei einigen Katzen zu brennen, und die orale Variante scheint fьrchterlich zu schmecken.
Fьr die injizierbare Darreichungsform werden normalerweise 0,5 bis 1 mg pro kg Kцrpergewicht der Katze angegeben. Eine 4,5 kg schwere Katze wьrde daher 2,25 bis 4,5 mg bekommen.
Fьr die orale Darreichungsform werden normalerweise 1 mg pro kg Kцrpergewicht empfohlen. Safety, pharmacokinetics and use of the novel NK-1 receptor antagonist maropitant (Cerenia) for the prevention of emesis and motion sickness in cats (2008) Hickman M. A ., Cox S. R ., Mahabir S ., Miskell C ., Lin J ., Bunger A ., McCall R. B ., Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 31(3) pp220-9 schreiben: „Die Ergebnisse weisen darauf hin, dass Maropitant ein effektives, gut vertrдgliches und sicheres Antiemetikum fьr Katzen ist bei einer Dosis von 1,0 mg/kg. “ Eine 4, 5 kg schwere Katze wьrde danach 4,5 mg bekommen. Die meisten Menschen scheinen die 16 mg Darreichungsform zu kaufen und teilen sie dann entsprechend auf (bei einer 4,5 kg schweren Katzen entsprдche das einem Viertel).
Die Tabletten sollten nicht in sogenannten Pill Pockets verabreicht werden (das sind Leckerlis, in denen man die Tabletten verstecken kann), oder ins Futter gegeben werden, da das dazu fьhren kann, dass das Medikament nicht ausreichend vom Kцrper aufgenommen wird but some people do give them this way.
Drs Foster & Smith verkauft vier 16mg-Tabletten zu US$7 , 99.
Der Hersteller empfiehlt, dass Maropitant Hunden nur ьber einen kurzen Zeitraum verabreicht werden sollte, maximal fьnf Tage hintereinander. Einige Menschen haben es bei ihren Katzen einige Tage lang eingesetzt, dann eine Pause gemacht und es anschlieЯend wieder eingesetzt. Plumbs Veterinary Drug Handbook weist darauf hin, dass das Medikament unter solchen Umstдnden mindestens 48 Stunden lang ausgesetzt werden sollte. In der oben genannten Studie mit Katzen, wurde es 15 Tage lang hintereinander verabreicht, ohne dass es zu Problemen kam. Ich weiЯ, dass nach dem Lesen dieser Studie einige Menschen ihren Katzen Maropitant ьber einen lдngeren Zeitraum als fьnf Tage gegeben haben und keine Nebenwirkungen bemerkten. Lassen Sie sich von Ihrem TA ьber die beste Vorgehensweise beraten.
Maropitant Neben- und Wechselwirkungen
Mцgliche Nebenwirkungen sind Erbrechen, Lethargie, Durchfall, Zuckungen und Speicheln. Maropitant sollte nicht eingesetzt werden, wenn im Magen-Darmbereich eine Blockade oder Verstopfung vorliegt. Bei Leber- oder Herzerkrankungen sollte es nur mit Vorsicht eingesetzt werden. (it may increase the risk of arrhythmias). Drugs has more information.
The European Medicines Agency schreibt (unter 4.8 Seite 9) , dass „ Maropitant nicht gleichzeitig mit Kalziumkanalblockern eingesetzt werden sollte, da es eine Affinitдt zu den Kalziumkanдlen hat. ” The University of Zьrich Institute for Veterinary Pharmacology and Toxicology schreibt das ebenfalls. Im Prinzip bedeutet das, dass Maropitant nicht mit Kalziumkanalblockern wie Amlodipin (Norvasc oder Istin, die hдufig verwendet werden, um Bluthochdruck bei Katzen zu behandeln) gemeinsam verabreicht werden sollte. „Gleichzeitig“ hat eine ziemlich vage medizinische Bedeutung . Es bedeutet, wдhrend der gleichen Zeitspanne , aber i n diesem Kontext weiЯ ich nicht genau , worauf sich die EMA bezieht, meinen sie z.B. zur selben Zeit oder am selben Tag? Beide Medikamente werden in der Regel einmal tдglich verabreicht, denn sie haben eine lange Wirkungsdauer. Ich vermute, wenn Sie sie beide am selben Tag geben aber zwцlf Stunden getrennt (z.B. eine am Morgen, die andere am Abend), dann wдre das wahrscheinlich machbar, aber fragen Sie dazu Ihren TA.
The European Medicines Agency weist auЯerdem dringend darauf hin, dass sofortige medizinische Hilfe aufgesucht werden sollte, wenn Maropitant in die Augen gerдt. The University of Zьrich Institute for Veterinary Pharmacology and Toxicology warnt ebenfalls vor Augenirritationen.
Pfizer product information sheet (tablets) erwдhnt, dass Maropitant nur ьber einen Zeitraum von fьnf Tagen verabreicht werden darf. Sie schreiben weiter, dass Maropitant eine Wechselwirkung mit Phenobarbital eingehen kann, das zur Kontrolle einer Epilepsie verabreicht wird und auch mit nicht-steroidalen Entzьndungshemmern .
Veterinary Partner bietet einige Information ьber den Einsatz von Maropitant bei Hunden an und erklдrt etwas mehr ьber den Mechanismus. Sie fьhren aus, dass Maropitant mit Phenobarbital, das zur Behandlung einer Epilepsie eingesetzt wird, in Wechselwirkung treten kann.
Drs Foster and Smith haben ein Informationsblatt ьber den Einsatz von Maropitant bei Hunden.
The Veterinary Teaching Hospital at Colorado State University sucht Freiwillige fьr eine Studie zur Behandlung von Ьbelkeit und Erbrechen von CNI-Katzen. Katzen, bei denen eine chronische, stabile CNI diagnostiziert wurde, und die heikel mit dem Fressen sind, an Ьbelkeit und Erbrechen leiden, sind potentiell qualifizierte Kandidaten fьr diese Studie. Katzen mit noch weiteren Erkrankungen sind dafьr ungeeignet.
Die Katzen werden zu Beginn kцrperlich untersucht, auЯerdem wird ein Blutbild der klinischen Chemie angefertigt. Die an der Studie teilnehmenden Katzen erhalten tдglich ьber einen Zeitraum von zwei Wochen entweder Maropitant oder ein Placebo. Nach zwei Wochen werden die Katzen erneut ein zweites Mal kцrperlich untersucht, und es wird wiederum ein Bluttest (Klinische Chemie) veranlasst. Wдhrend der Studie werden die Besitzer gebeten, tдglich ein Tagebuch ьber das Verhalten und andere Details ihrer Katzen zu fьhren. Die Besitzer bekommen die begleitenden TA-Besuche und Blutuntersuchungen kostenlos. Jeder daran teilnehmende Tierarzt erhдlt - um seine Unkosten zu decken - 100 US$ Belohnung fьr jede Katze, die daran teilnimmt.
Wenn Sie daran teilnehmen mцchten, dann nehmen Sie mit Kontakt auf mit Dr Jessica Quimby on 970-297-5000 oder bei jquimby@colostate.edu .
Metoclopramid ist ein verschreibungspflichtiges Medikament. Seine Wirkung besteht darin, dass es die Magenkontraktionen reguliert. Dadurch kann es bei Ьbelkeit helfen, die aufgrund eines Mangels an Motilitдt im Magen entsteht. Da Metoclopramid auch die Blut-Hirnschranke ьberwinden kann, wirkt es auch auf das Hirn und kontrolliert das Ьbelkeitsgefьhl.
Pet Place gibt Informationen ьber gastrische Motilitдtsprobleme bei Katzen (Sie mьssen sich nicht registrieren, klicken Sie bei dem Pop-up-Fenster unten einfach auf „close").
Tierarzneimittelkompendium der Schweiz bietet Informationen auf Deutsch ьber Metoclopramid.
Arzneimittelkompendium Zьrich bietet Informationen ьber Metoclopramid a n .
Metocolopramid ist als 10 und 5 mg Tabletten erhдltlich oder als Flьssigkeit. Es ist auch als Injektion erhдltlich in 5 mg/ml, 2 ml oder 10 ml Ampullen. Es muss 20 bis 30 Minuten vor einer Mahlzeit gegeben werden.
Eine ьbliche Dosis wдren 0,2 bis 0,5 mg pro kg alle sechs bis acht Stunden. Eine 4,5 kg schwere Katze wьrde also 1 bis 2 mg pro Medikation bekommen. Lassen Sie sich von Ihrem TA beraten.
Metoclopramid Neben- und Wechselwirkungen
Bei Metoclopramid kцnnen verschiedene Nebenwirkungen auftreten wie Verstopfung, Hyperaktivitдt und Unruhe oder Schlдfrigkeit, seltener wird auch von Zuckungen berichtet.
Reglan senkt auch die Schwelle fьr Anfдlle, daher sollte es Katzen, die zu Anfдllen neigen, nicht verabreicht werden. Drugs schreibt, dass es auch das Risiko von Bronchospasmen bei Asthmatikern erhцh en kann . Das intravenцs verabreichte Metoclopramid kann eine n Bluthochdruck verschlechtern.
Am 26. Februar 2009 warnte die US Food and Drug Administration vor dem "Dauereinsatz dieser Produkte [gemeint sind Medikamente, die Metoclopramid enthalten] bei der Behandlung von Magen-Darm-Stцrungen". Der Grund ist, dass einige Medikamente, die Metoclopramid enthalten, in Zusammenhang gebracht werden mit tardiven Spдtdyskinesien, das sind unwillkьrliche, unregelmдЯige, schnelle und kurzzeitige Muskelkontraktionen der Gesichtsmuskulatur und des Kцrpers, die sogar anhalten kцnnen, wenn das Medikament nicht mehr verabreicht wird. Eine dieser willkьrlichen Bewegungen, die die FDA erwдhnt, ist Lippenschmatzen (obwohl hier erwдhnt werden sollte, dass Lippenschmatzen/-lecken bei CNI-Katzen normalerweise durch zuviel Magensдure oder Ьbelkeit, eine Anдmie oder Austrocknung verursacht wird). Die FDA empfiehlt daher, dass Medikamente, die Metoclopramid enthalten, nicht lдnger als drei Monate eingesetzt werden sollten. Diese Warnung bezieht sich zwar auf Menschen, aber ich wьrde diese Warnung mit Ihrem TA besprechen, wenn Sie Metoclopramid lдnger als drei Monate geben mцchten.
Ich empfahl frьher, Metoclopramid mit mindestens zweistьndigem Abstand zu Famotidin (Pepcid) oder Ranitidin (Zantic) zu verabreichen. Der Grund war, dass laut Plumb's Veterinary Drug Handbook Metoclopramid sich mit diesen anderen Medikamenten verbinden kцnnte und deren Wirksamkeit dadurch herabgesetzt wird. In der neuesten Ausgabe von Plumb’s wird diese Anforderung jedoch nicht mehr erwдhnt. Es sieht demnach so aus, als mьsste man nun doch keinen zeitlichen Abstand mehr zu diesen Medikamenten einhalten.
Pet Place hat ebenfalls einige Informationen. (Sie mьssen sich nicht registrieren, klicken Sie bei dem Pop-up-Fenster unten einfach auf „close".
Drs Foster and Smith informieren ьber mцgliche Nebenwirkungen. Sie weisen auch darauf hin, dass Metoclopramid PABA дhnelt, dem Hauptbestandteil vieler Sonnenschutzmittel. Menschen, die dagegen allergisch sind, sollten daher Metoclopramid nicht anfassen.
Die nachfolgenden Medikamente sind fьr den Einsatz bei CNI-Katzen ungeeignet.
Bitte geben Sie nicht Pepto-Bismol. Es enthдlt ein Salicylat, дhnlich dem in Aspirin. Katzen kцnnen es nicht gut verstoffwechseln, daher kann es schon in kleinen Dosen tцdlich sein.
Pet Education bietet mehr Information an ьber Pepto-Bismol.
Einige TД empfehlen Antazida wie Tums, Mylanta (USA) oder Gelusil Lac, Talcid, Rennie, Maaloxan (Deutschland) u.a. Einige dieser Medikamente wirken gut bei CNI-Katzen als Phosphatbinder, aber hдufig sind sie nicht stark genug, um den Magensдureьberschuss ausreichend zu kontrollieren. AuЯerdem enthalten einige Produkte Magnesium . Das ist nicht angebracht bei CNI-Katzen, die ohnehin zu hohen Magnesiumspiegeln tendieren.
Diese Seite zuletzt ьberarbeitet: 12. April 20 15
Links auf dieser Seite zuletzt ьberprьft: 19. April 2012
DIE BEHANDLUNG IHRER KATZE OHNE TIERДRZTLICHE UNTERSTЬTZUNG KANN EXTREM GEFДHRLICH SEIN.
Ich habe mich sehr bemьht sicherzustellen, dass alle Informationen auf dieser Website richtig sind. Aber ich bin KEIN Tierarzt, nur eine ganz normale Person, die mit drei ihrer Katzen chronische Nierenerkrankungen durchlebt hat.
Diese Website dient nur Informationszwecken und nicht dazu, Diagnosen zu erstellen oder eine Katze zu behandeln. Bevor Sie irgendeine der hier beschriebenen BehandlungsmaЯnahmen ausprobieren, MЬSSEN Sie einen Tierarzt aufsuchen und sich professionellen Rat fьr die richtige Behandlung Ihrer Katze holen und ihre individuellen Anforderungen. Sie sollten auch keine der hier beschriebenen Behandlungsarten ohne Kenntnis und Zustimmung Ihres TA einsetzen.
Wenn Ihre Katze Schmerzen zu haben scheint, oder es ihr nicht gut geht, dann verschwenden Sie bitte keine Zeit im Internet, sondern suchen Sie sofort Ihren TA auf.
Copyright © Tanyas CNI Webseite 2000-201 5 . Alle Rechte vorbehalten.
Diese Webseite wurde mit Microsoft Software erstellt, daher sieht sie im Internet Explorer am besten aus. Mir ist bekannt, dass sie bei anderen Browsern nicht immer so gut dargestellt wird, aber ich bin keine IT-Expertin, daher weiЯ ich leider nicht, wie ich das дndern kцnnte. Natьrlich wьnschte ich, sie wьrde ьberall gut aussehen, aber mein Fokus ist darauf gerichtet, die darin enthaltenen Informationen bereitzustellen. Wenn ich Zeit habe, werde ich versuchen, auch in anderen Browsern die Darstellung zu verbessern.
Sie dьrfen sich eine Kopie dieser Website zu Ihrer eigenen Information machen und/oder Ihrem Tierarzt eine Kopie geben. Aber diese Website darf ohne Genehmigung der Seiteninhaberin weder reproduziert noch ausgedruckt werden, nicht im Internet, noch in anderen Medien. Ьber den Button Kontaktaufnahme kцnnen Sie sich mit mir in Verbindung setzen. In dieser Website steckt sehr viel Arbeit und Liebe. Bitte bestehlen Sie mich nicht, indem Sie mein Urheberrecht verletzen.
Sie kцnnen diese Seite gerne verlinken. Machen Sie dann aber bitte deutlich, dass es sich um einen Link handelt und nicht um Ihre eigene Arbeit. AuЯerdem wдre ich dankbar, wenn Sie mir einen Hinweis auf diesen Link schicken wьrden.
Die hier aufgefьhrten Verknьpfungen zu anderen Internetseiten (Hyperlinks) stellen Informationsangebote fremder Anbieter dar, auf deren Inhalte ich keinen Einfluss habe. Insbesondere ьbernehme ich keinerlei Haftung fьr den Inhalt oder den Wahrheitsgehalt dieser Internetseiten.
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий